Beyond Cultures: Exploring the Fermented Frontier
KRUPA KOESTLINE
CEO and Consultant Chemist, KKT Labs, Florida, USA
ABSTRACT: I've always been fascinated by how science often takes its cue from nature, drawing on its wisdom to create innovative solutions. This is especially true in the realm of skincare, where fermentation—a process as old as time itself—has become a revolutionary force. Join me as we explore the fermented frontier, where tradition meets modern science to deliver skincare products that are both powerful and gentle.
??????????????????
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”
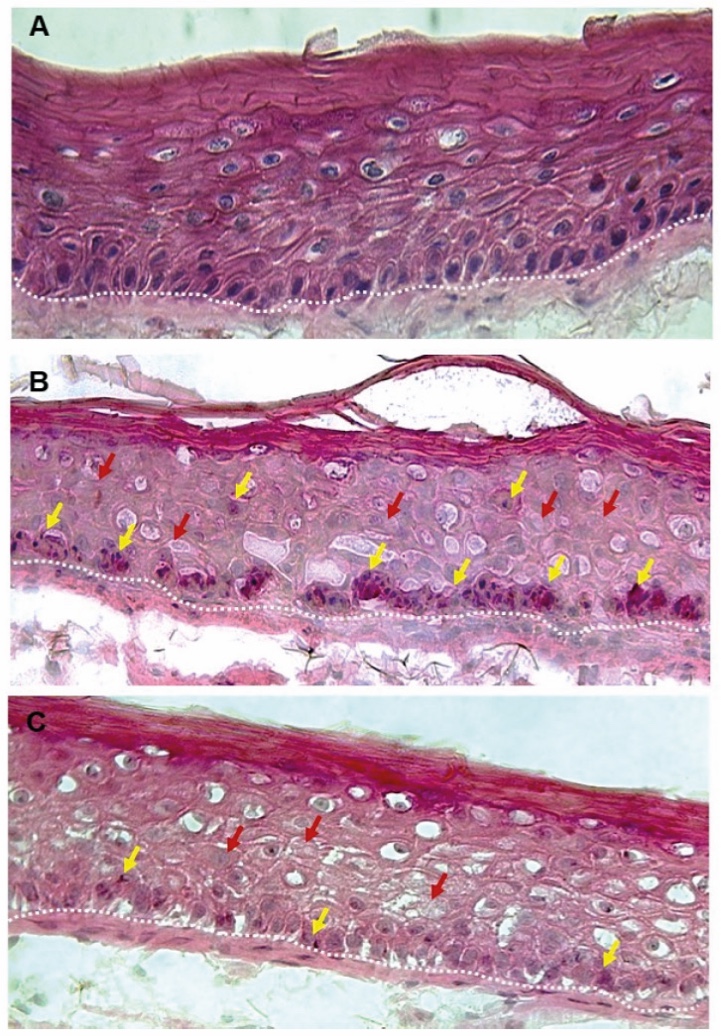
Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
What is Fermentation?
In simple terms, fermentation is an anaerobic metabolic process where carbohydrates, like lactose, are partially oxidised to generate energy for cells, producing lactic acid as a byproduct. Imagine taking a bowl of sugar and watching it transform into a powerhouse of beneficial compounds, just like how grapes turn into wine. Here's a quick breakdown:
Carbohydrates → Acids + Energy (CO₂ + Metabolites)
This biochemical magic increases the potency, penetration, and preservation of the resulting compounds, making them particularly valuable in skincare. Fermented cosmetics work harmoniously with the skin, offering several benefits that unfermented products can't match. The skin, unlike the intestines, lacks enzymes to aid in digestion. This is where fermentation steps in, breaking down the molecular structure of ingredients, making nutrients more concentrated and easier for the skin to absorb. The process also produces beneficial amino acids and antioxidants.
Fermentation mimics the skin’s natural processes, supporting it without causing disruption, thus reducing the likelihood of sensitivity. The sugar and fruit acids in fermented ingredients help to moisturise the skin. Consequently, these actives protect and enhance the skin’s metabolism, making it stronger and healthier.
Types of Fermented Ingredients in Skincare
Depending on the type of fermentation and the specific microorganisms involved, a wide array of metabolites, known as postbiotics, are produced. These are rich in nutrients like vitamins, amino acids, lactic acid, polysaccharides, and beta-glucans, all of which nourish the skin and support the immune system.
1. Functional Products from Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation is a cutting-edge technology that uses genetically modified microorganisms as 'cell factories' to produce specific compounds. By inserting genes into the DNA of microorganisms, scientists can control the production process, optimising fermentation conditions to produce enzymes, vitamins, and other compounds. This method offers a sustainable alternative to traditional ingredients sourced from non-renewable resources like petrochemicals or unsustainable plants and animals.
2. Ferment Filtrates, Extracts and Lysates
The microbial biomass itself can serve as an ingredient, with cells intact or minimally processed for enriched cell contents. Paraprobiotics and postbiotics are key forms of biofermented ingredients, often referred to as ferment extracts, filtrates, and lysates.
- Paraprobiotics (1): These consist of inactivated microbial cells, including both structural components (like peptidoglycans, surface proteins, and cell wall polysaccharides) and metabolites (such as proteins, peptides, bacteriocins, and organic acids).
- Postbiotics (1): These are composed exclusively of metabolites produced during fermentation, without the structural components of the microbial cells.
Benefits of Fermented Ingredients
Fermentation imparts several unique benefits to skincare ingredients, enhancing their properties and efficacy:
- Increased Potency and Nutrient Content: Fermentation maintains the integrity of the ingredients, unlike traditional cosmetics that may lose effectiveness due to high-temperature processing. Fermented ingredients boast higher concentrations of nutrients, such as amino acids, peptides, and antioxidants.
- Enhanced Skin Compatibility: Fermented ingredients typically have a more acidic pH, which aligns better with the skin’s natural acidity. This ensures that the ingredients support the skin’s natural processes without causing irritation or sensitivity.
- Improved Penetration and Absorption: Fermentation breaks down the molecular structure of ingredients into smaller molecules, allowing them to penetrate the skin more deeply and quickly (2). This deep penetration ensures that beneficial nutrients reach the lower layers of the skin, enhancing their efficacy.
- Anti-inflammatory and Soothing Properties: Fermented ingredients are rich in enzymes that can soothe and prevent skin inflammation. These enzymes help eliminate harmful bacteria on the skin and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, preserving the skin’s balance and health.
Considerations in Biofermentation
Effective biofermentation in skincare requires careful consideration of several factors:
Microorganism Selection and Optimisation
Choosing the right microorganism is crucial for successful biofermentation. Strains must be selected based on their ability to produce the desired compounds efficiently. Optimisation of growth conditions, such as temperature, pH, and nutrient availability, ensures maximum yield and activity of these microorganisms. Recent developments and high-throughput methods of strain selection, adaptation, screening, and engineering have enabled innovators to iterate new strains with greater speed and precision.
Substrate Selection and Fermentation Conditions
The substrate, or raw material used in fermentation, significantly influences the outcome. Natural substrates, such as plant extracts or sugars, are commonly used. Controlling fermentation conditions, including aeration, agitation, and fermentation time, is essential to produce high-quality fermented ingredients. Although strain development in this sector often utilises biotechnological tools like gene editing and genetic engineering, significant advancements can still be achieved through traditional adaptation and breeding strategies, enhanced by cutting-edge genomic insights.
Feedstock Optimisation
Feedstocks provide essential nutrients for microorganisms during fermentation, significantly contributing to the process's flexibility and adaptability. However, feedstocks are also a major cost factor. Most fermentation processes currently use standardised, refined, sugar-based feedstocks, which have a proven track record in food and industrial biotechnology. Due to the large volumes required, feedstocks represent a substantial input cost, with high shipping expenses further increasing overall costs.(3)
Downstream Processing Techniques
After fermentation, the bioactive compounds must be extracted and purified. Downstream processing techniques like filtration, centrifugation, and drying are employed to isolate and stabilise the desired ingredients. These steps are critical to ensure the purity and efficacy of the final product.

Trendy Fermented Ingredients
Now, let's delve into some of the most exciting and unique fermented ingredients on the market today. These have been specially selected for their innovative nature and the distinct benefits they bring to skincare.
Lactobacillus/Rye Flour Ferment (4)
Fermented actives using multi-strain fermentation approach, like the Lactobacillus/Rye Flour Ferment (4) elevates the beneficial properties of organic rye through ecosystemic fermentation. Unlike single-strain methods, this approach utilises a multi-strain consortium of natural lactic acid bacteria, providing a wider array of beneficial agents for the skin. The result is a range of products that help resurface the skin, promote the growth of beneficial skin commensals, and reduce biofilm formation, leading to visibly smoother, blemish-free skin.
Gentiana Lutea Root Extract (and) Sphingomonas Ferment Extract (5)
This COSMOS-certified, upcycled, and microbiota-friendly active ingredient features a wild yellow gentian root extract enhanced through fermentation with rare, cold-tolerant bacteria from aerobiota. The ferment extract (5) enhances skin moisture, plumpness, and firmness by upregulating HA synthesis and CD44 synthesis, crucial for skin barrier reinforcement and proper hyaluronic acid diffusion. In the development of this active, the supplier takes a unique comprehensive approach, addressing the entire skin ecosystem, enhancing host/microbiota interactions for healthier, hydrated skin.
Bacillus Ferment (6)
Derived from an Italian thermal spring, this bacillus ferment is designed to alleviate skin inflammation caused by external stress, ageing, and poor diet. It leverages the unique properties of thermal spring microbiota (hydrobiome), highlighting the potential of these bioactive compounds to treat dermatological issues, enhance UV protection, strengthen barrier function, and prevent skin ageing.
Hydrolyzed Rhodophyceae Extract (7)
This extract takes a refined approach to the first signs of skin ageing, leveraging the extremophilic properties of the red alga Galdieria sulphuraria, which thrives in Iceland’s hot sulfur springs. This remarkable alga can survive in extremely hostile environments with pH levels between 0 and 4 and extreme temperatures. The extract harnesses these properties through a sustainable fermentation process to create a highly effective active ingredient. Invitro and Invivo(8) results show reduction in cell senescence, increase in cell energy levels, and a boost in the production of procollagen I and hyaluronic acid under stress. Studies conducted in urban environments show that the extract reduces wrinkles, improves skin smoothness, and enhances skin tone evenness, making it a multifaceted solution for modern skincare.
Schizophyllan Ferment Extract (9)
This ferment is based on the Schizophyllum commune mushroom, known for its potent anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties. The ferment includes both intracellular and extracellular polysaccharides, offering enhanced skincare benefits. In studies, such an extract (10) has shown remarkable efficacy in reducing oxidative stress, increasing SOD enzyme activity. Some studies performed by the supplier implies in this ability to provide superior moisturization compared to hyaluronic acid.
Successful Incorporation of Fermented Ingredients in Consumer Products
Several skincare brands have successfully integrated fermented ingredients into their products, showcasing enhanced efficacy and consumer satisfaction. Here are a few noteworthy examples:
Launched in the 1980s, SK-II’s (11) hero product, the Treatment Essence (11), stands as a paragon in the realm of fermented skincare. At the heart of this iconic product is Galactomyces ferment filtrate (12) a unique bio-ingredient derived from the yeast fermentation process. Rich in vitamins, amino acids, minerals, and organic acids, this ferment mimics the natural moisturising factors found in healthy skin (12). This essence is celebrated for its ability to promote cell renewal, enhance moisture retention, and improve skin texture, resulting in a radiant and youthful complexion. SK-II's pioneering use of fermented ingredients has set a high standard for efficacy and innovation in the beauty industry (12).
Lancôme(13)’s Advanced Génifique Youth Activating Serum(13) incorporates a blend of prebiotics and probiotics to bolster skin health. This serum features Bifida Ferment Lysate and Lactobacillus Ferment to support and strengthen the skin's microbiome. By enhancing the skin's natural barrier and promoting a balanced microbiome, this serum improves skin resilience, smoothness, and radiance(13).
Cultured Biomecare’s(14) Biome One Cleansing Balm utilises fermented red ginseng along with prebiotics and postbiotics to nurture the skin's microbiome. Fermented red ginseng is known for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (15). By incorporating prebiotics and postbiotics, this cleansing balm supports the skin's natural defences and maintains a healthy, balanced complexion.
Symbiome’s (16) One Restorative Cream features fermented olive leaf extract and postbiotics. Sourced from the Amazon rainforest, these ingredients are carefully chosen for their ability to nourish and rejuvenate the skin. The fermentation process enhances the bioavailability of the active compounds, ensuring that the skin receives maximum benefits(2).
TULA Skincare’s(17) 24-7 Moisture Hydrating Day & Night Cream is formulated with Bifida Ferment Lysate, prebiotics, and a blend of nourishing superfoods. This cream has shown in clinical studies to provide comprehensive hydration and support the skin's natural balance, making it a versatile addition to any skincare routine.
The Future of Biofermentation
Biofermentation has emerged as a transformative technology in the personal care industry, offering sustainable and effective solutions for skincare. The incorporation of fermented ingredients not only meets consumer demands for natural and clean products but also enhances the efficacy and sustainability of skincare formulations. As technology advances, the future of biofermentation promises even greater innovation and benefits across various industries.
The integration of fermentation technology into skincare offers a multitude of benefits, from increased nutrient density to enhanced skin compatibility and deep penetration. By harnessing the power of microorganisms, fermented cosmetics provide potent, effective, and sustainable solutions that meet the demands of modern consumers for natural and high-performing skincare products. This symbiotic relationship between fermented ingredients and the skin not only boosts skin health but also supports the growing trend towards environmentally friendly and scientifically backed beauty solutions.
As biofermentation technology continues to advance, its applications will expand beyond personal care into other industries, offering sustainable and innovative solutions to a wide range of challenges. The future of biofermentation is bright, promising continued growth and development in creating ingredients that are not only effective but also environmentally friendly.

Conclusion
The future of cosmetics lies in the continued evolution of holistic approaches which represents a transformative shift in the industry, merging scientific advancements, natural ingredients, and wellness principles. By understanding and embracing the interconnectedness of these elements, the cosmetics industry can cultivate products that not only enhance external beauty but also contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and the planet.
The interplay between beauty from within and topical cosmetics is the key for future products. The integration of biotechnology and green chemistry is revolutionizing cosmetic formulations, offering sustainable and biocompatible alternatives.
Developers can implement blockchain to trace the journey of ingredients from source to product. Nevertheless, the efficacy of the natural products should be scientifically proven. Marketers can communicate transparency as a brand value, and parallelly educate consumers by highlighting how specific ingredients contribute to radiant and healthy skin.
By embracing the synergy between these approaches and leveraging scientific advancements, the cosmetics industry can provide consumers with comprehensive beauty solutions that cater to both internal and external dimensions of beauty.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
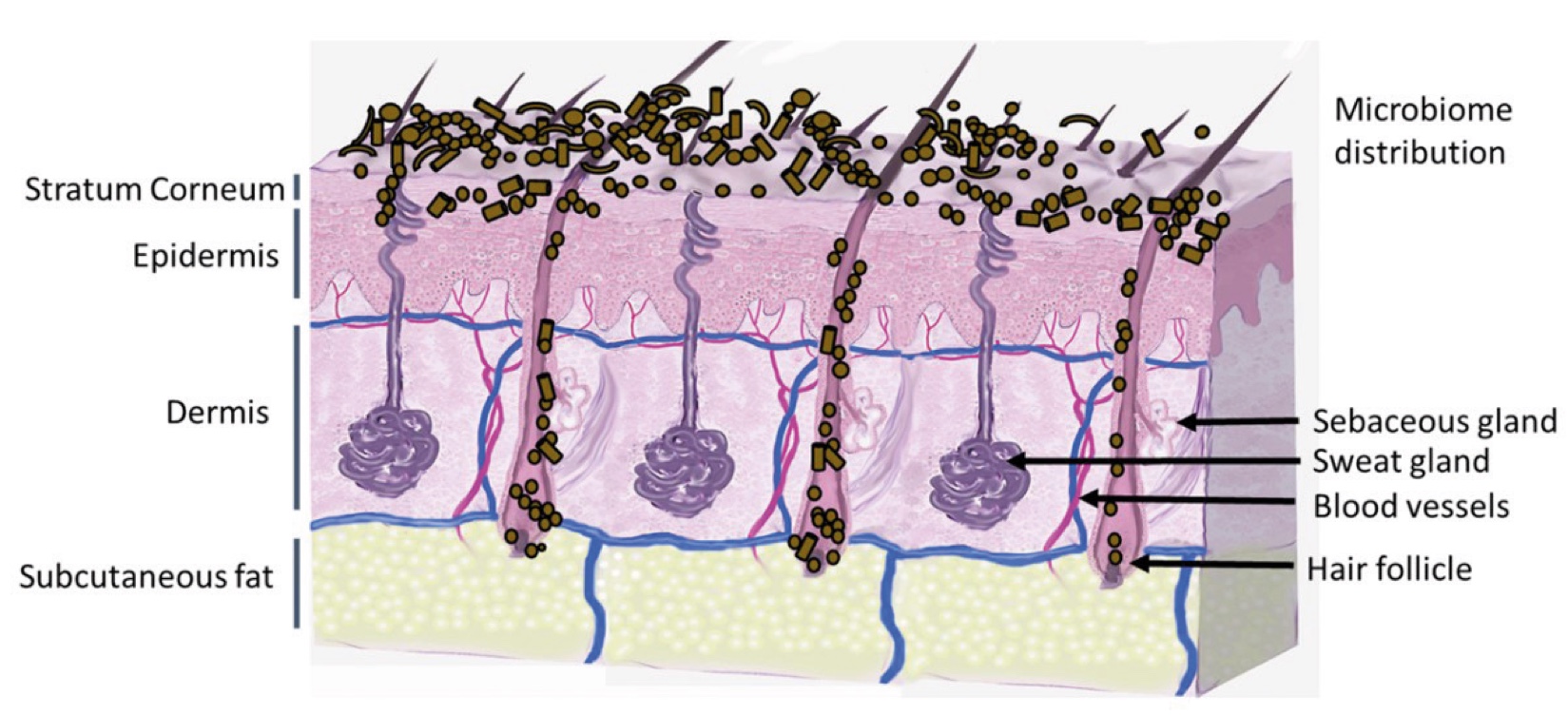
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0963996920305275
- https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/29/5/1018
- https://gfi.org/science/the-science-of-fermentation/
- https://personal-care.evonik.com/en/products-solutions/new-active-ingredients
- https://www.greentech.fr/en/holobiosys/
- https://www.lubrizol.com/Personal-Care/Products/Product-Finder/Products-Data/Zenerity-biotech-ingredient
- https://www.clr-berlin.com/products/cutiguard-clr/
- https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%3A6%3A14222982/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A157596938&crl=c
- https://dermegen.com/DermaTive-snow-mushroom-ferment/
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Musaalbakri-Manan-2/publication/322758642_Comparative_Evaluation_of_Schizophyllum_commune_Extracts_as_Potential_Cosmeceutical_Bio-Ingredient/links/5a7713d9aca2722e4df0fb61/Comparative-Evaluation-of-Schizophyllum-commune-Extracts-as-Potential-Cosmeceutical-Bio-Ingredient.pdf
- https://www.sk-ii.com/product/essence/facial-treatment-essence/160ml?gad_source=1&gclid=Cj0KCQjw3tCyBhDBARIsAEY0XNkjfy2IYGRQ3vyIhBZSXM1gs956umr6Fod0JG3ldePH6IJKDmyIYH4aAigwEALw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds
- https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=132770
- https://www.lancome-usa.com/skincare/advanced-genifique-face-serum/3605533117217.html?GeoRedirectOff&gad_source=1&gclid=Cj0KCQjw3tCyBhDBARIsAEY0XNk7rQTIka80QpNiCWefKl3_USUH3MFDBcNy8cE8QvcW0_6DbofDPGYaAqpAEALw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds
- https://www.culturedbiomecare.com/products/biomeonecleansingbalm
- https://www.ulprospector.com/en/na/PersonalCare/Detail/30848/725746/Fermentoil-Complex?st=1&sl=404797971&crit=a2V5d29yZDpbQ2FuZGlkYSBCb21iaWNvbGEvR2x1Y29zZS9NZXRoeWwgUmFwZXNlZWRhdGUgRmVybWVudF0%3d&ss=2&k=Candida|Bombicola%2fGlucose%2fMethyl|Rapeseedate|Ferment&t=Candida+Bombicola%2fGlucose%2fMethyl+Rapeseedate+Ferment
- https://www.symbiome.com/
- https://tula.com/products/hydrating-day-night-cream

