
Insights in Innovative Textures
on
Skin care
peer-reviewed
Insights:
Innovative Textures
ARIADNA GRAU-CAMPISTANY*, PATRICIA CARULLA, LAIA FARRÉ, SILVIA PASTOR
*Corresponding author
Lipotrue, Barcelona, Spain
ABSTRACT: Due to the favourable characteristic of cyclic peptides, such as the higher stability and lower toxicity, they are attractive candidates for the development of therapeutics. Protein misfolding increases with age, and the accumulation of these misfolded or unfolded proteins causes ER stress. An existing linear peptide was cyclized in order to find a novel active ingredient, which was able to act on this ER stress by improving the UPR efficiency while boosting collagen. Overall, improving the aging skin and balancing the fluctuation between morning and evening wrinkles.
??????????????????
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”

Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
Textures play an important role in cosmetics, contributing to improving sensory characteristics of a product and the user’s experience.
They can be seen as the appearance, or consistency of a formulation, therefore they can influence the acceptance of a product, and consequently its effectiveness.
Studying innovative textures can be crucial to obtain better formulations, aiming at increasing sensory aspects, acceptance and performance.
It is equally important to develop specific tests to evaluate and characterize sensory aspects of formulations to understand consumer preferences.
This scientific review is therefore composed of two parts:
1) Textures: The first study focuses on a new specific polymer used in a sun care formulation. In particular, the polymer properties were studied to obtain efficient sunscreen products with pleasant textures. The second article is about testing two different types of oils used to obtain colloidal hydrogels. Subsequently, the impact of the ingredients on differences in texture was explored. The third study is about the exploitation of new generation of bio-based ingredients in cosmetics. In this case, expert sensory evaluation and instrumental characterization were employed.
2) Sensory testing: The first article reports the results of tests on the cosmetic application of different vegetable oils. In this case, volunteers were also involved in a study which allowed to comprehend the influence of fatty acids on the sensory profile of formulations.
The second article focuses on the characterization and sensory evaluation of a formulation made of roasted coffee oil microcapsules. Assessors received one kit with the formulations and a notebook with instructions to carry out the tests at home. The main goal was to assess if the ingredient could be viable for dermocosmetics with sensory acceptance.
The third article is about characterizing sensorial attributes of topical formulations, by using a rapid, quantitative, and objective approach. In particular, machine learning models were leveraged to predict textural attributes and skin feel.

TEXTURES
Scientific online resources as Pubmed and Google Scholar were used to retrieve articles of interest. To screen for the most advanced research, articles were selected from year 2023 to year 2024 with the following keywords: innovative textures, cosmetics textures, new textures cosmetics
New formulation technology to boost sun protection
Authors:
Hélène Meaudre1, Odile Aubrun1, Jean-Baptiste Boitte1, Stéphane Douezan1, Martin Josso1, Danielle Le Verge1, Pascale Renoux1, Gaelle Rondepierre2
Affiliations:
1L'Oréal R&I, Chevilly-Larue, France.
2L'Oréal R&I, Saint-Ouen, France.
Int J Cosmet Sci. 2023 Dec; 45(6):802-814. DOI: 10.1111/ics.12889. Epub 2023 Oct 6 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37718248/
Objective: As every skin type worldwide is concerned by photoprotection, with consumers preferring cosmetic elegant and efficient sunscreen products, we aim at developing the most performant and desirable sun care products.
Methods: We selected an interesting polymer, abbreviated AAHCP and designed scanning electron cryomicroscopy (cryoSEM), small angle and wide angle X-ray scattering and confocal laser scanning microscopy studies to understand its behaviour in solution and in simplex sun care formulations. This allowed us to develop innovative sunscreen formulation technology that was demonstrated by in vitro and in vivo photoprotection methods. Comprehensive photoprotection evaluations were made on the fully developed sun protection product.
Results: We observed the polymer oil structuring properties as well as its ability to form small and stable droplets in simplex emulsions. In vitro and in vivo sun protection factor (SPF) measurements demonstrated the sun protection boosting efficacy of AAHCP polymer in several emulsions or as a stand-alone emulsifier. This formulation technology also allowed to filtering system concentration optimization. Use-test performed on a fully developed AAHCP-based sunscreen validated its optimal performances as well as its ideal cosmetic features, with non-sticky, non-greasy perception and invisible skin result.
Conclusion: For the first time, thanks to a new specific polymer creating a new type of emulsion, we succeed in reconciliate in a single sun care product maximal SPF efficacy, resistance to numerous stresses and optimal sensoriality.
Physicochemical study of aqueous dispersions of organogel particles: Role of the ingredients and formulation process leading to colloidal hydrogels
Authors:
Bérénice Duret12, Emile Perez1, Sarah Arneodo2, Bruno Payré3, Céline Picard2, Sophie Franceschi1
Affiliations:
1Université de Toulouse, UPS/CNRS, IMRCP, 118 route de Narbonne, 31062 Toulouse, France
2Université du Havre, URCOM, EA 3221, FR CNRS 3038, 25 rue Philippe Lebon B.P. 540, 76058 Le Havre Cedex, France
3Centre de Microscopie Electronique Appliquée à la Biologie, Faculté de Médecine Rangueil, 113 route de Narbonne, 31062 Toulouse Cedex, France
Colloids and surfaces A: physicochemical and engineering aspects Vol.661, 2023, 130905, ISSN 0927-7757, DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130905.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/
Abstract
The cosmetics industry is always looking for new textures, both from a performance and sensory point of view. In this field, emulsions remain an important source of inspiration. In this study, aqueous dispersions of organogel particles were obtained by hot emulsification (T°>Tgel), and cooling (T°<Tgel). Two oils were tested, sweet almond oil and phytosqualane, using 12-hydroxystearic acid (HSA) as an organogelator, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA80) as a stabilizer. A preservative agent (Saliguard® COS) and an antioxidant (Tocopherol) were also used. Under the same preparation conditions, two completely different textures were obtained depending on the oil: a stable dispersion of organogel particles for sweet almond oil and a colloidal hydrogel for phytosqualane. In this study, we were able to understand the impact of the ingredients on these differences in texture, and propose different mechanisms of formation. The important role played by the preservative agent at the water/oil interface of the droplets, during the gelation step, was demonstrated. Such adsorption, depending on the polarity of the oil, can modify the anchoring of the dispersing agent (PVA80) and lead during the gelation to a destabilization of the droplets by coalescence and to the formation of a colloidal hydrogel. These results highlight the possible formation of colloidal hydrogels from particles of organogels and open the way to new textures in the cosmetic or pharmaceutical field.
Sensory signature of lignins, new generation of bio-based ingredients in cosmetics
Authors:
Caroline Hadjiefstathiou123, Audrey Manière1, Joan Attia1, Florian Pion2, Paul-Henri Ducrot2, Michel Grisel3, Ecaterina Gore3
Affiliations:
1IFF-Lucas Meyer Cosmetics, Campus Eiffel-Massy - Bat. Edison 13 Rue Ella Maillart 91300 Massy, France
2Université Paris-Saclay, INRAE, AgroParisTech, Institut Jean-Pierre Bourgin (IJPB), 78000 Versailles, France
3Université Le Havre Normandie, Normandie Univ, URCOM, UR 3221, F-76600 Le Havre, France
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, Volume 260, Part 1, March 2024, 129399
DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129399
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
article/abs/pii/S0141813024002022
Abstract
Lignins represent a high interest in cosmetics as promising multifunctional ingredients. Despite this, uncovering the sensory profile of lignin-based emulsions has remained an unexplored frontier.
This study aims to bridge this gap by employing expert sensory evaluation and instrumental characterization to assess the sensory attributes of lignin-based emulsions. A comparative analysis with commercial tinted products and discrimination among lignin derivatives were integral components of the research. Results underscored the distinctive sensory properties of lignin emulsions, exhibiting significantly higher “Integrity of shape” (7.0 ± 0.1) compared to commercial products (4.8 ± 0.1). Additionally, lignin emulsions displayed longer play-time until skin absorption (4.3 ± 0.1), contrasting with the quicker absorption of commercial products (2.7 ± 0.4) and their shorter play-time. Depending on application requirements, lignin derivatives offer formulators a versatile sensory toolbox.
Discrimination of lignin emulsions on certain texture properties was achieved using various instrumental tools. Despite the complex formulation of commercial products compared to lignin emulsions, similar texture properties were observed, showcasing lignins' potential to replace multiple ingredients in tinted cosmetics. Beyond their established antioxidant, anti-UV, anti-bacterial, and emulsifying properties, this study reveals additional advantageous sensory properties of lignins, positioning them as promising plant-based sensory ingredients in sustainable cosmetic applications.
SENSORY ANALYSIS
Scientific online resources as Pubmed and Google Scholar were used to retrieve articles of interest. To screen for the most advanced research, articles were selected from year 2023 to year 2024 with the following keywords: sensory evaluation, texture analysis cosmetics
Preparation and sensory evaluation of gels based on silicone copolymers/acrylic copolymers incorporating different vegetable oils
Authors:
Rousilândia de Araujo Silva 1, André Luís Morais Ruela 2, Maria Eugenia de
Oliveira Mamede 3, Neila de Paula Pereira 1
Affiliations:
1 Department of Medicament, Faculty of Pharmacy, Federal University of Bahia, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
2 Department of Pharmacy, School of Pharmacy, Federal University of Ouro Preto, Ouro Preto, Minas Gerais, Brazil
3 Department Food Science, Faculty of Pharmacy, Federal University of Bahia, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
Industrial Crops and Products Volume 193, 2023, 116147, ISSN 0926-6690,
DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.116147
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
article/abs/pii/S0926669022016302
Abstract
Fixed vegetable oil is one of the most used plant derivatives for cosmetic application, especially in skin products, due to its fatty acid composition, which are similar to the skin's natural components. Therefore, it is important to study the cosmetic application of new vegetable oils, and how their fatty acid constitution influences the product’s sensory profile. In this study, topical gel formulations were prepared by cold processing method using copolymers derived from silicone and acrylic acid incorporating Gueroba (GGE) and Macaúba (GM) vegetable oils and comparing them to Sweet Almond Oil (GA), considered to have a gold standard. The formulations were evaluated for physical stability, texture profile, rheology and sensory analysis through the Sorting Test. All gel formulations allowed the incorporation of vegetable oils and remained stable, without variation in their organoleptic characteristics; the GM formulation presented the best spreadability performance, with Eimax 3739.8 mm2. As for texture, the GGE formulation recorded lower Firmness values (4.73 g). Rheological evaluation determined that all formulations showed pseudoplastic behavior, with the presence of thixotropy and better recovery for GM formulation, which is characteristic of semi-solid formulations for topical use. Sensory analysis in volunteers indicated that the samples have a similar spreadability profile. The results obtained indicate that the fatty acids influence the sensory profile of the formulations, being a differential factor in the sensory performance of cutaneous preparations destined to skin care.
Characterization and Sensory Evaluation of a Cosmeceutical Formulation for the Eye Area with Roasted Coffee Oil Microcapsules
Authors:
Böger, Bruna Raquel 1, Audrey Alesandra Stinghen Garcia Lonni 2 , and Marta de Toledo Benassi 1
Affiliations:
1 Departamento de Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos, Universidade Estadual de Londrina, Rodovia Celso Garcia Cid Km 380, Londrina 86057-970, Brazil
2 Departamento de Ciências Farmacêuticas, Universidade Estadual de Londrina, Avenida Roberto Koch 60, Londrina 86039-440, Brazil
Cosmetics 2023, 10(1), 24, DOI: doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics10010024
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/10/1/24
Abstract
The objective of this work was to characterize a cosmeceutical formulation for the eye area with roasted coffee oil microcapsules (MOF) and evaluate the acceptance and effects of its use by consumers. MOF had 3% microcapsules produced by complex coacervation; a basic formulation (BF) was used for comparison. The addition of microcapsules did not affect the pH (4.52), density (0.99 g mL−1), consistency (0.77 N s), and viscosity index (0.25 N s) of the formulation. However, a reduction in spreadability, firmness, and cohesiveness was observed. The 58 assessors received one kit with the formulations and a notebook with instructions to carry out the tests at home. They were instructed to apply the cream for 28 days and evaluate the attributes of application and treatment effects on 7-point category scales. The effect of oil addition observed in the physical tests was not sensorially perceived for spreadability and tackiness (6.0 and 5.6, respectively), indicating approval and easiness of application. The perception of the benefits (increase in smoothness, hydration, firmness, elasticity, and skin general appearance, and reduction in signs of fatigue and wrinkles/fine lines) was similar comparing MOF and BF. In conclusion, the coffee oil microcapsule is a viable ingredient for dermocosmetics with sensory acceptance.
Predicting textural attributes and frictional characteristics of topical formulations based on non-linear rheology
Authors:
Febin Cyriac, Tee Xin Yi, Pui Shan Chow
Affiliations:
Institute of Sustainability for Chemicals, Energy and Environment (ISCE2), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), 1 Pesek Rd, 627833, Singapore
Biotribology, Volumes 35–36, 2023, 100249, DOI: 10.1016/j.biotri.2023.100249
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/
Abstract
A number of analytical procedures (Spectrum Descriptive Analysis (SDA), Quantitative Descriptive Analysis (QDA), and Check All That Apply (CATA)) are used for characterizing sensorial attributes of topical formulations. However, these techniques are evaluated by expert panels/consumers, which are subjective, expensive and time consuming. Despite widespread use of these methods, the techniques do not necessarily aid in the development of innovative formulations and understanding of consumer liking. In addition, the hedonic attributes of a product can significantly dominate the sensation. Therefore, a more rapid, quantitative, and objective approach is required for understanding the formulation factors that governs sensory perception at different points of consumer application. Rheological evaluations of topical formulations were carried out under steady and oscillatory (SAOS and LAOS) rheology using a commercial rheometer. Friction measurements were performed using an in-house built tribometer on non-biological skin model to investigate how surface properties are influenced by application of different topical formulations. Further, a broad range of instrumental texture measurements was performed to characterize the formulations. Principal component analysis was used for dimensionality reduction of the instrumental data. Supervised machine learning was performed on the closely related PCA parameters to develop predictive models. We identified physical parameters relevant to different perceptual attributes by comparing a range of commercial topical formulations with various compositions using rheological and tribological methods. Multi-variate machine learning models were developed where several key instrumental textural attributes and skin feel could be predicted from data obtained from linear and non-linear rheological measurements. Our study shows rheological analysis based on a few material parameters can be effectively used for predicting instrumental sensory attributes that is of relevance to consumer care industry. The machine learning models may benefit development of innovative formulations, valorisation of new materials and serve as a platform for mapping commercial formulations for product optimization. The models can likely shorten design cycle time by screening through large volume of formulations and short list only those with highest potential to be evaluated by a very specialized and expensive human test panel.
Conclusion
The future of cosmetics lies in the continued evolution of holistic approaches which represents a transformative shift in the industry, merging scientific advancements, natural ingredients, and wellness principles. By understanding and embracing the interconnectedness of these elements, the cosmetics industry can cultivate products that not only enhance external beauty but also contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and the planet.
The interplay between beauty from within and topical cosmetics is the key for future products. The integration of biotechnology and green chemistry is revolutionizing cosmetic formulations, offering sustainable and biocompatible alternatives.
Developers can implement blockchain to trace the journey of ingredients from source to product. Nevertheless, the efficacy of the natural products should be scientifically proven. Marketers can communicate transparency as a brand value, and parallelly educate consumers by highlighting how specific ingredients contribute to radiant and healthy skin.
By embracing the synergy between these approaches and leveraging scientific advancements, the cosmetics industry can provide consumers with comprehensive beauty solutions that cater to both internal and external dimensions of beauty.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
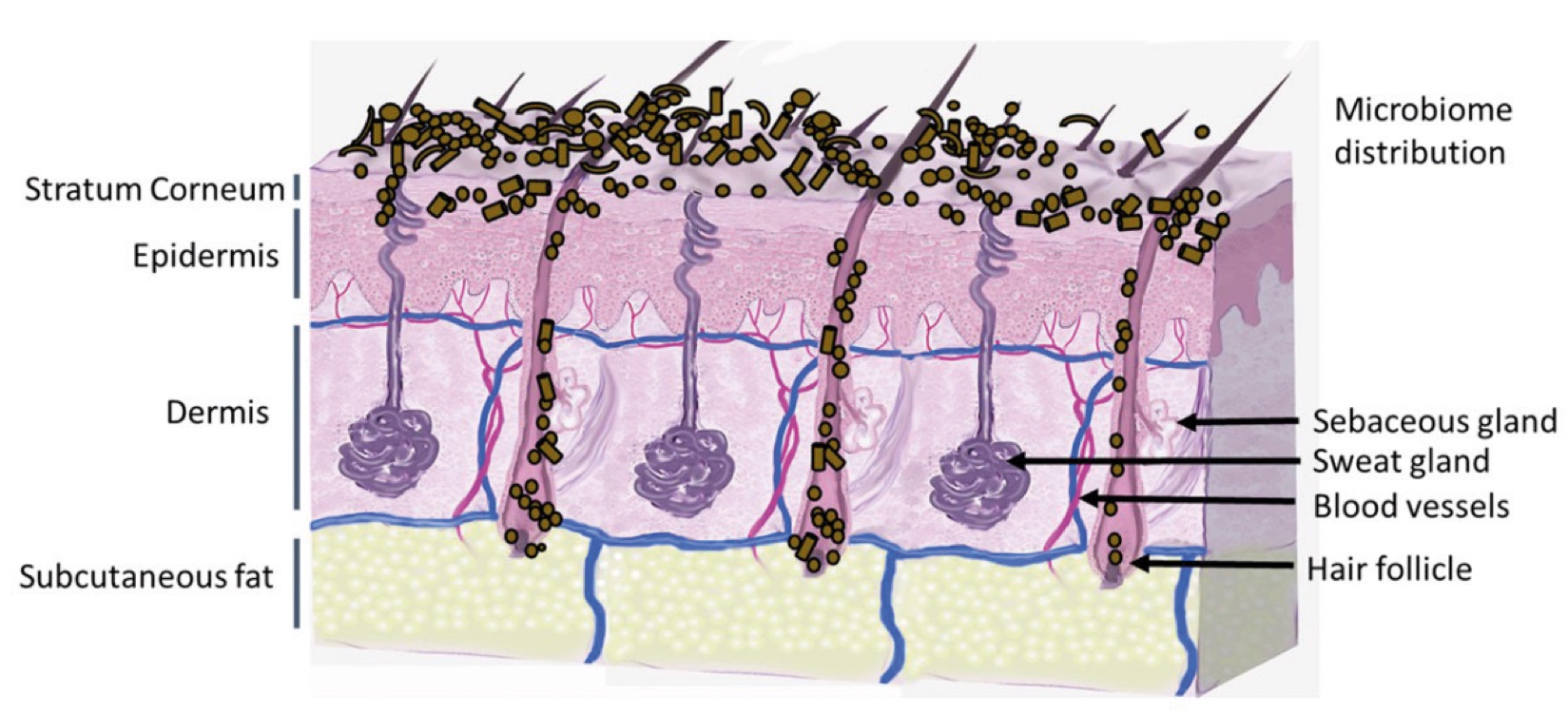
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- Zompra AA, Galanis AS, Werbitzky O, Albericio F. Manufacturing peptides as active pharmaceutical ingredients. Future Med. Chem. 2009; 1, 361-377.
- Claro B, Bastos M, Garcia-Fandino R. Design and applications of cyclic peptides. Peptide Application in Biomedicine, Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 2018; 87-129.
- Walter, P., and Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science. 2011; 334, 1081–1086.
- Chadwick, SR., and Lajoie, P. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Coping Mechanisms and Lifespan Regulation in Health and Diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019; 21;7:84.
- Naidoo, N., Ferber, M., Master, M., Zhu, Y., and Pack, A. I. Aging impairs the unfolded protein response to sleep deprivation and leads to proapoptotic signaling. J. Neurosci. 2008; 28, 6539–6548.
- Fields GB and Noble RL. Solid-phase peptide synthesis utilizing 9-fluorenylmethozycarbonyl amino acids. International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research. 1990; 35: 161-214.
- Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012; 13:89-102.
- Pandya UM, Manzanares MA, Tellechea A, Egbuta C, Daubriac J, et al. Calreticulin exploits TGF-β for extracellular matrix induction engineering a tissue regenerative process. FASEB J. 2020; 34: 15849-15874.
- Van Duyn Graham L, Sweetwyne MT, Pallero MA, Murphy-Ullrich JE. Intracellular calreticulin regulates multiple steps in fibrillar collagen expression, trafficking and processing into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 2010; 5: 7067-78.
- Gold LI, Eggleton P, Sweetwyne MT, Van Duyn LB, Greives MR, et al. Calreticulin: non-endoplasmic reticulum functions in physiology and disease. FASEB J. 2010; 24: 665-83.
- Li, JH, Huang, XR, Zhu, HJ, Johnson, R, Lan, HY. Role of TGF-beta signaling in extracellular matrix production under high glucose conditions. Kidney Int. 2003; 63(6): 2010–2019.
- Murata, H, Zhou, L, Ochoa, S, Hasan, A, Badiavas, E, Falanga, V. TGF-beta3 simulates and regulates collagen synthesis through TGF-beta1-dependen and independent mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol. 1997; 108(3):258-62.
- Tsukahara K, Moriwaki S, Hotta M, Fujimura T, Kitahara T. A study of diurnal variation in wrinkles on the human face. Arch Dermatol Res. 2004; 296:169-74.
- Tsukahara K, Takema Y, Moriwaki S, Fujimura T, Imokawa G. Dermal fluid translocation is an important determinant of the diurnal variation in human skin thickness. Br J Dermatol. 2001; 145:590-6.
