COLUMN: FORMULATION SPELLS - WHAT AI DOESN’T KNOW YET
KEYWORDS —
With the hope to give cues on formulation through this new column, in a global beauty market nonetheless crowded yet demanding products meant to innovate, while keeping up with regulatory compliance, environmental concerns, and the latest trends, we pursue skilfully formulated products, from the INCI list and beyond, going through technical insights and creativity magically merging. That’s why Formulation Spells: what AI cannot do…yet.
ISNTREE - Yam Root Vegan Milk Toner
For this issue, the column features Yam Root Vegan Milk Toner by the Korean skincare brand Isntree. It's an interestingwater-thin hybrid product between an emulsion-based serum and a toner, a popular format in Asian Countries, where it is known as milky toner, differentiating it from its "fellow" toners, mists and serums. Upon rubbing it onto the skin it is watery and fast-absorbing, leaving a thin, non-sticky layer of lipids. In order to gain a deeper understanding of the formula from a technical standpoint, the product underwent several tests in our laboratory (Tab. 1).
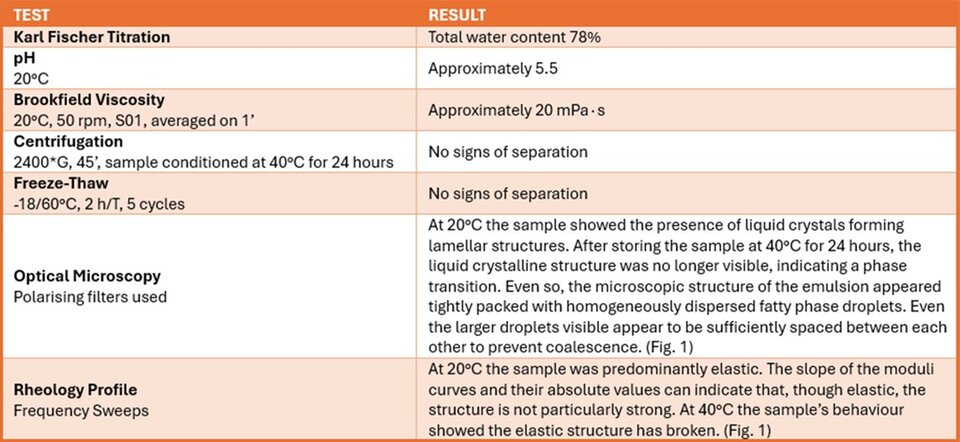
Table 1. Tests and results
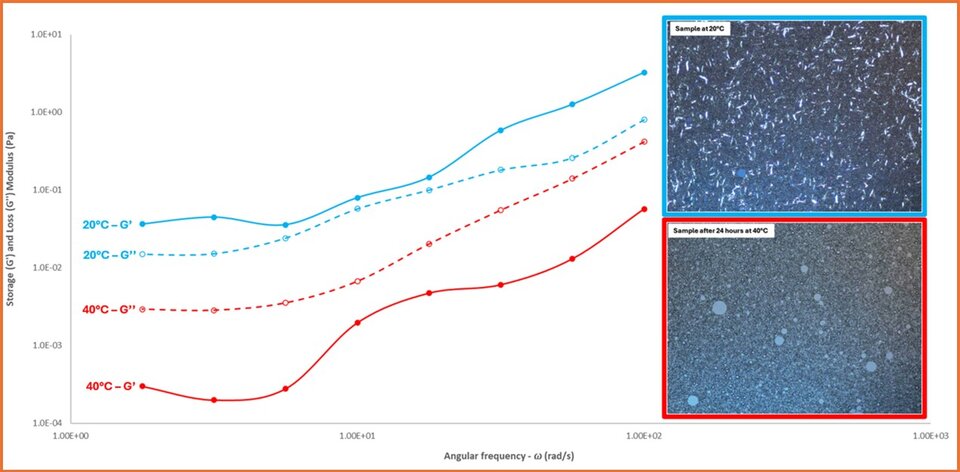
Figure 1. Frequency Sweep results and microscopy photographs
When forming an O/W emulsion, the non-ionic polymeric emulsifier Inulin Lauryl Carbamate (ILC),through its hydrophobic lauryl side chains strongly adsorbs onto the fatty droplets with limited or no desorption because of its high molecular weight, creating intense elastic repulsions, whereas its loops of polyfructose get highly hydrated in the aqueous phase building strong steric barriers between the inner and the outer phase. By solely acting at the interface, ILC does not affect viscosity, while it still does increase the system's yield value. On the other hand, the lipopeptidic anionic surfactant Sodium Surfactin (SSF), characterised by a head-tail structure, presents a head unusually made of a rather large peptide ring that exposes two carboxyl groups which enable hydrogen bonds between peptide heads, as well as some degree of interaction with other molecules. This mechanism allows SSF to form particularly strong and large micelles that could eventually create liquid crystalline structures under appropriate conditions (e.g. composition, fatty phase concentration and polarity).
On top of its activity as an emulsifier and surfactant, SSF has also been shown to deliver skin benefits (e.g. anti-inflammatory) and increase skin penetration of hydrophilic ingredients (1).
To better understand how ILC and SSF interact between each other and with other ingredients in the context of this particular system, including the formation of various liquid crystalline phases, the construction of complex phase diagrams would be necessary.
From the results of microscopy and rheological analyses (Tab. 1) (Fig.1), we assume that emulsion stability at 20°C is ensured by the lamellar structures, as also confirmed by the frequency sweeps, whereas at 40°C SSF becomes more mobile, supposedly starting to detach from the fatty phase, and eventually disrupting the lamellar structures. Nevertheless, thanks to its molecular weight and strong lipophilic anchoring, desorption of ILC does not occur, still ensuring emulsion stability via a powerful steric barrier, as shown by the rapid physical stability tests (Tab.1). Remarkably, ILC and SSF can be effectively used at low level (0.1-0.5%), both individually and combined, minimally impacting the sensory profile of the product.
As per the above, it's pretty evident that the pivotal ingredients in forming and supporting such O/W emulsion are ILC and SSF, obviously along with the water phase and a fatty phase of approximately 3-6%.
Notably, as per the rheological profile (Fig. 1) Sodium Polyacrylate may have been used below its critical aggregation concentration, not sufficient to impart a more resistant elastic structure, thus unlikely to contribute to the product structure and stability. Hence, it might have been added through other raw materials rather than intentionally.
Despite ILC and SSF working synergistically to form such a stable low-viscosity emulsion, finding alternative ways to obtain a similar format could be quite challenging, yet not impossible. Anyway, a worldwide Mintel analysis conducted across all beauty categories (time span 2000 to date) has revealed that combinations of ILC and SSF have been used in approximately 0.1% of product launches (the vast majority of which are Japanese, Chinese, and Korean).
Back to the product, from the efficacy point of view, it features several active ingredients. Starting from the skin barrier strengthening Hydrogenated Lecithin and Cholesterol liposomes dispersed in a hydroglyceric mediumand entrapping lipophilic actives (Ceramide NP and Deoxyphytantriyl Palmitamide MEA dissolved in Caprylic/Capric Triglyceride likely along with Stearic Acid). Highly effective humectants Glycerin and Butylene Glycol able to attract and retain moisture (supposedly also introduced as solvents for plant extracts); non-reducing disaccharide Trehalose acting as antioxidant as well as humectant; Panthenol reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and exerting antioxidant activity, consequently healing and protecting the skin from inflammation (from the INCI it is not possible to distinguish if D-Panthenol was used or the racemic form DL-Panthenol whose activity is approximately half that of D-Panthenol). Emollient vegetable oils Limnanthes Alba Seed Oil, Helianthus AnnuusSeed Oil, Macadamia Ternifolia Seed Oil, Argania Spinosa Kernel Oil helping nourish and maintain the skin protective barrier. The compositional profile of each vegetable oil varies depending on the plant source and extraction methods and includes mainly acylglycerides, fatty acids, tocopherols, unsaponifiable fractions and other minor compounds. Noteworthy, the limited production, high price and demand of Argania Spinosa Kernel Oilmake it susceptible to deliberate adulteration with vegetable oils. Its high percentage of stearic acid (4.3–7.2%) allows differentiates it from other vegetable oils except from sunflower oil, which seems to have a similar percentage of stearic acid (2.5–7.0%) (2). Last but not least, various Asian plant extracts such as Dioscorea Japonica Root Extract ranked in first position on the ingredient list and claimed at 80% on label. However, we are supposedly dealing with a low-concentration dry extract reconstituted in water, as Karl Fischer titration revealed a total water content of 78% (Tab. 1).
Despite their efficacy, plant extracts are generally present in formulations at low concentrations as they can affect colour, odour, and viscosity, hence it's required to be able to properly manage them avoiding stability issues.
Regarding Dioscorea japonica, or Andong yam, it is one of the over 600 species from the Dioscorea genus. Extracts from Dioscorea roots contain several phytochemicals such as steroidal sapogenins primarily diosgenin, phytosterols, phenolic compounds, polysaccharides, anthocyanins and flavonoids. They reportedly display antioxidant activity related mainly to radical-scavenging capacity and anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting key inflammatory pathways NF-κB and MAPK signalling (3). While Dioscorea Japonica Root Extract is safely used as a skin conditioning ingredient, Dioscorea Villosa (wild yam) Root Extract, equally used in personal care products, was assessed in 2023 by the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel (4), emphasising the importance of a specified process to produce a stable extract with a narrow range of diosgenin content (upper limit of 3.5%), as it is a well-known precursor for the synthesis of steroid hormones and its potential estrogenic effects. Nelumbo Nucifera Root Extract contains active compounds providing moisturising and anti-ageing benefits. Still under investigation, flavonoid glycosides (e.g. Kae-3-Rob) reportedly showed strong activity as whitening agents (measured by tyrosinase inhibition and DOPA-oxidase inhibition assays) and anti-wrinkle effects (checked by elastase inhibition assay) (5). High in flavonoids and mucilagesHibiscus Esculentus Fruit Extract provides moisturising and anti-ageing benefits. Derived from seaweeds Undaria Pinnatifida Extract and Laminaria Japonica Extract are rich in fucoidan, shown to promote collagen synthesis.
It's interesting to highlight their unique idea of blending Soybean Seed Extract, Coconut Fruit Extract, Rice Extract, Sweet Almond Seed Extract, Oat Meal Extract and Malt Extract to mimic "milks" inspired by popular vegetable drinks, appealing to consumers.
Citric Acid ensures a pH of approximately 5.5 (Tab.1). 1,2-Hexanediol, Caprylyl Glycol, Hydroxyacetophenone, Pentylene Glycol are multifunctional ingredients mainly used for their antimicrobial properties. Despite contributing to the product's overall stability, the chelating agent Disodium EDTA, because of its environmental persistence and toxicity to aquatic life, would have been better replaced by eco-friendly alternatives.
Lastly, a brief note to appreciate the use of non-coated, environment-friendly FSC-certified packaging made with recycled green tea paper & soy ink, other than wash-off labels that easily separate from the container with water.
In a nutshell, an interesting example of a product conceived thinking out of the box and merging technical insights with creativity. What AI doesn't know…yet…is that formulating is "a kind of magic".

References and notes
- Int J Cosmet Sci 2024(00):1-15 https://doi.org/10.1111/ics.12957
- Molecules 2023(28):1818 https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041818
- Molecules 2022(27):2530 https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082530
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel (2023): Safety Assessment of Dioscorea Villosa (Wild Yam) Root Extract as Used in Cosmetics https://www.cir-safety.org/sites/default/files/RR_Wild%20Yam.pdf
- Int J Mol Sci 2023(24):16571 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316571


