Innovation, Vision and Science in the Cosmetic Industry
MARÍA VICTORIA LOVELLE IGLESIAS
Innovation Specialist at Beauty Cluster, Barcelona, Spain
ABSTRACT: This article provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in science and technology that are shaping the cosmetic industry. It underscores the importance of continued research and innovation to meet the evolving needs of consumers and improve their quality of life.
??????????????????
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”
Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
Introduction
Advances in skin and hair treatments are reshaping the cosmetic industry, driven by scientific innovation. Researchers are uncovering new mechanisms to better understand skin and hair, which has led to the development of safer and more effective products. Skin diseases such as Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis are receiving significant attention, with researchers exploring novel drug delivery methods and probiotics to manage these conditions. Identifying biomarkers and genetic mechanisms is also crucial for personalized treatments. For instance, Camellia Sinensis L. Extract is being studied for its anti-inflammatory effects in treating Atopic Dermatitis.
Similarly, advancements in hair loss treatments, particularly for conditions like Alopecia areata and Androgenetic alopecia, focus on new therapies, such as oxytocin receptor agonists, exosome-derived RNAs, and mitochondria research. The cosmetic industry is evolving as scientists revisit established ingredients like retinoic acid to explore their potential for treating hair loss and skin conditions, highlighting the importance of continued innovation in this field.
Beauty Cluster: Driving Innovation in Cosmetic Industry
On February 20th and 21st, Barcelona was the epicenter of cosmetic innovation with the celebration of the "Beauty Innovation Days" congress. This event, organized by the Beauty Cluster, a Spanish association with more than 250 companies in the cosmetics, perfumery, and personal care sector, was established as a key meeting point to promote innovation in the cosmetic industry.
The congress brought together a wide range of companies from across the cosmetic value chain. International experts shared their perspectives on cosmetic science and innovation, trends, and market research, offering a comprehensive vision of the sector's future.
Talking about trends and innovation in the industry, I would like to highlight key insights into skin diseases, emerging technologies in hair care, and the pivotal role of innovation. We now turn to explore the significant advances in skin and hair treatments, where cutting-edge research is driving the development of more effective solutions.
Advances in Skin Treatments
The cosmetic industry is in constant evolution, driven by innovation, vision, and science. In recent years, we have witnessed significant advances in our understanding of skin and hair, leading to the development of exciting new products and treatments.
Science is playing an increasingly important role in the cosmetic industry. Researchers are exploring new techniques, strategies, and mechanisms to better understand skin and hair, paving the way for the development of new ingredients and formulations that are safer and more effective. It highlights the importance of innovation and vision in developing new products and treatments that address the evolving needs of consumers.
Skin is the largest organ of the human body, and its function is to protect it from external agents while also providing a certain level of permeability. However, skin can also suffer diseases affecting it like Psoriasis Skin and Atopic Dermatitis. The difference between these two diseases is that Psoriasis Skin is an autoimmune disorder, characterized by an accelerated cycle of cell renewal which leads to the accumulation of cells on the skin's surface while Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by immune dysregulation and excessive cytokine production.
Atopic dermatitis is constantly studied and new perspectives for treatment are seeking to reduce or avoid these symptoms. Some of the new strategies are focused on finding new drugs for specific targets and using new nano-technology-based drug delivery (1).
The mechanisms which trigger Atopic Dermatitis are not defined and science is constantly looking for new strategies to understand them. One strategy could be toidentify the potential Atopic Dermatitis protein biomarkers. Scientists are exploring new strategies to tackle skin diseases. One approach involves identifying novel candidate plasma proteins for the pathogenesis and treatment of atopic dermatitis (2). A second strategy could be to try to identify gene modules that trigger these diseases. By understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying this condition, researchers hope to develop more effective treatments. This approach can offer different methods to support diagnosis and guide a personalized treatment (3).
In addition to these new strategies, the role of microbiota in atopic diseases is also being investigated, with studies exploring the potential of probiotics as a novel therapeutic approach (4). They found that microbiota plays a role in the pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. Probiotics are live bacteria that can provide health benefits when consumed. They are believed to help modulate skin microbiota, which plays a role in skin health.
Cosmetic products help to treat and reduce the symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis, providing hydration and avoiding some ingredients in the formulas, such as alcohol or soaps. A good strategy to improve cosmetic treatments is to study new benefits for well-known ingredients used in cosmetic products. Camellia Sinensis L. Extract is a good example, which is explored as a treatment for Atopic Dermatitis by its impact on inflammatory responses in keratinocytes. In conclusion, Kim, M.J., Yang, Y.J., Min, GY. et al. found that Camellia Sinensis L. Extract might be potential candidate for Atopic Dermatitis treatment due to its efficacy as an anti-inflammatory effect (5).
Advances in Hair Treatment
Similar situations happen when we talk about hair diseases. Some of them can affect the scalp (dandruff or greasy hair), the hair fiber (hair breakage or dry hair), or the hair growth cycle like Alopecia areata or Androgenic alopecia. These two are diseases that cause hair loss, and they should not be confused. Whilst Areata Alopecia is an autoimmune disorder characterized by reversible hair loss without losing the hair follicle, Androgenetic Alopecia is, in the other case, the most common form of non-cicatricial hair loss which it affects a significant percentage of men and women. Heredity, hormones, environmental inflammation, and oxidative stress are some of the factors that trigger this disease. Hair loss begins when the growth rate changes, the anagen phase shortens, and there is premature entry into the catagen phase, reducing the anagen-to-telogen ratio (6).
Researchers are exploring innovative approaches to combat hair loss. One such strategy involves investigating the effects of oxytocin receptor agonists on hair growth promotion. By targeting the oxytocin pathway, scientists aim to develop new drugs for alopecia (7).
Another promising way is the study of exosome-derived long non-coding RNA AC010789.1, which has shown potential in accelerating hair follicle stem cell growth against androgen alopecia (8). Additionally, research on mitochondria and hair follicle development is shedding light on potential therapeutic interventions for androgenetic alopecia (9).
The cosmetic industry is entering a new era of innovation. Science provides new insights into skin and hair, helping to develop innovative products and treatments. In the case of hair, and following the same strategy for skin, well-known ingredients are being studied to explore new benefits. Retinoic acid is studied for its role in activating hair follicle stem cells and inhibiting the pathogenesis of Androgenetic alopecia (10).
Retinoic acid is a controversial ingredient. It has many benefits for treating skin and hair, but its use in cosmetic products is banned by the European Commission. Other retinoic acid derivatives are permitted and regulated for cosmetic use, and studying their benefits could be a good way to continue exploring this strategy.
Conclusion
The cosmetic industry is entering a new era of innovation, while science provides new insights into skin and hair, which are being used to develop new and exciting products and treatments. In the future, we can expect to see even more advances as science continues to push the boundaries of what is possible.
In conclusion, it is necessary to emphasize the importance of science in driving innovation in the cosmetic industry. As our understanding of skin and hair biology deepens, the possibility of personalized cosmetic treatments becomes increasingly attainable.
Innovation is the lifeblood of the cosmetic industry and companies that do not innovate quickly fall behind. Innovation can take many forms, from developing new products and services to creating new ways to reach consumers.
Conclusion
The future of cosmetics lies in the continued evolution of holistic approaches which represents a transformative shift in the industry, merging scientific advancements, natural ingredients, and wellness principles. By understanding and embracing the interconnectedness of these elements, the cosmetics industry can cultivate products that not only enhance external beauty but also contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and the planet.
The interplay between beauty from within and topical cosmetics is the key for future products. The integration of biotechnology and green chemistry is revolutionizing cosmetic formulations, offering sustainable and biocompatible alternatives.
Developers can implement blockchain to trace the journey of ingredients from source to product. Nevertheless, the efficacy of the natural products should be scientifically proven. Marketers can communicate transparency as a brand value, and parallelly educate consumers by highlighting how specific ingredients contribute to radiant and healthy skin.
By embracing the synergy between these approaches and leveraging scientific advancements, the cosmetics industry can provide consumers with comprehensive beauty solutions that cater to both internal and external dimensions of beauty.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
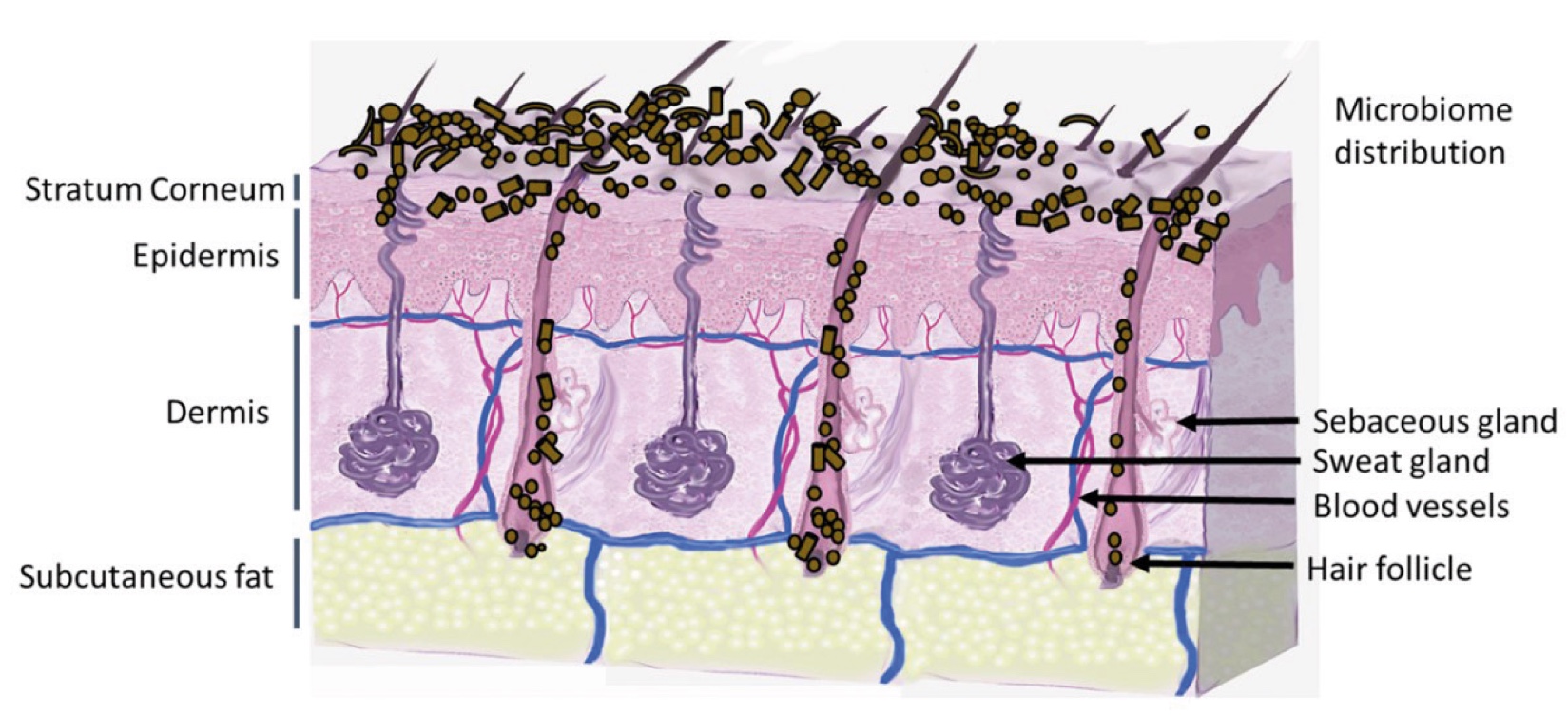
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- Pareek A, Kumari L, Pareek A, Chaudhary S, Ratan Y, Janmeda P, Chuturgoon S, Chuturgoon A. Unraveling Atopic Dermatitis: Insights into Pathophysiology, Therapeutic Advances, and Future Perspectives. Cells. 2024; 13(5):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050425
- Luo, C., Zhang, Y., Feng, Q. et al. Novel candidate plasma proteins for the pathogenesis and treatment of atopic dermatitis revealed by proteome-wide association study. Sci Rep 14, 30096 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-79906-x
- Seremet, T., Di Domizio, J., Girardin, A. et al. Immune modules to guide diagnosis and personalized treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Nat Commun 15, 10688 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-54559-6
- Petrillo F, Buonanno A, Fedi L, Galdiero M, Reibaldi M, Tamburini B, Galdiero E. Atopic Dermatitis and Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis: New Insights in the Analyses of Microbiota and Probiotic Effect. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(4):1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041463
- Kim, M.J., Yang, Y.J., Min, GY. et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Camellia sinensis L. extract as a potential therapeutic for atopic dermatitis through NF-κB pathway inhibition. Sci Rep 15, 2371 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-86678-5
- Gabriel Lazzeri Cortez, Karime Hassun, Luciana Ribeiro Patricio Linhares, Verena Florenço, Maria Valeria Bussamara Pinheiro, Mauricio Mendonça do Nascimento. Male androgenetic alopecia. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. 2025. ISSN 0365-0596, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abd.2024.08.004. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0365059624002605
- Kageyama, T., Seo, J., Yan, L. et al. Effects of oxytocin receptor agonists on hair growth promotion. Sci Rep 14, 23935 (2024).
- Chu S, Jia L, Li Y, et al. Exosome-derived long non-coding RNA AC010789.1 modified by FTO and hnRNPA2B1 accelerates growth of hair follicle stem cells against androgen alopecia by activating S100A8/Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Clin Transl Med. 2025; 15:e70152. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ctm2.70152
- Dong, Tr., Li, Yj., Jin, Sy. et al. Progress on mitochondria and hair follicle development in androgenetic alopecia: relationships and therapeutic perspectives. Stem Cell Res Ther 16, 44 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-025-04182-z
- Wen L, Fan Z, Huang W, Miao Y, Zhang J, Liu B, et al. Retinoic acid drives hair follicle stem cell activation via Wnt/β-catenin signalling in androgenetic alopecia. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025; 39: 189–201. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jdv.20000

