
Preservatives
Skin care
peer-reviewed
Future of Cosmetic Preservation: How green multifunctional ingredients enhance cosmetic safety while rebuilding consumer trust
VIKTORIA POTKO
Marketing manager, Minasolve, Belgium
ABSTRACT: Consumer awareness of cosmetic ingredients has grown significantly, leading to increased scrutiny of traditional preservation systems. While conventional preservatives have always played a crucial role in ensuring product safety and stability, shifting consumer preferences towards sustainability, transparency, and the clean beauty movement have driven demand for safer, naturally derived alternatives. In response, the industry is increasingly turning to green ingredients that offer both preservation efficacy and added skincare benefits. Among them, multifunctional ingredients have emerged as a particularly promising solution, creating conditions unfavourable to bacterial proliferation while providing additional skin care benefits.This article aims to explore the rise of multifunctional ingredients as natural preservation alternatives, highlighting their effectiveness, benefits, and role in shaping the future of cosmetic formulations while addressing consumer trust, transparency, and sustainability demands.
??????????????????
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”
Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
The cosmetic industry is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by increasing consumer scrutiny of product ingredients and a fundamental shift in beauty standards. Once focused primarily on product performance, today’s consumers evaluate cosmetics not only for their efficacy but also for ingredient transparency, ethical sourcing, and environmental impact — all without compromising on effectiveness. When it comes to business, the market has seen 27,000+ new FMCG product launches with at least one sustainability claim since January 2023 (1). Studies show that product efficacy, safety, and authenticity remain top priorities, with 85% of consumers willing to pay more for beauty products with proven benefits (2). Key purchasing drivers now include the presence of natural and organic ingredients, sustainable sourcing practices and product innovation. This growing awareness has heightened concerns over the environmental impact of cosmetic ingredients, particularly preservatives, which play a vital role in ensuring product safety and stability. In response, the industry is shifting its focus toward preservation systems that balance performance with sustainability, addressing the demand for more sustainable, ethical and efficient cosmetic formulations.
Cosmetic products, like any formulation containing water and organic or inorganic compounds, need effective preservation to prevent microbial contamination, ensuring consumer safety and extending shelf life. Whether stored on a shelf or actively used by consumers, cosmetic products must be safeguarded against potential microbial contamination and growth. Cosmetic preservatives market size exceeded USD 980 million in 2021 and is estimated to grow at over 8% CAGR between 2022 and 2028 (3). The global natural cosmetic preservatives market is projected to exceed USD 640 million by 2028 (4), driven by the growing use of natural ingredients in cosmetic formulations. The rising availability of natural alternatives to synthetic preservatives, coupled with increasing consumer awareness of the potential harm caused by chemical ingredients, is expected to boost demand for these products.
Evolution of preservative systems:
In the past, preservatives like parabens and phenoxyethanol were essential for ensuring product safety, but concerns about their potential risks have led to growing interest in natural alternatives. Among the most promising solutions are green multifunctional ingredients, which offer a dual benefit of preserving the product’s shelf life while enhancing the overall skincare experience. These multifunctional ingredients not only provide product protection but also align with the broader consumer demand for cleaner and more efficient beauty products. As a result, the cosmetic industry is embracing a new era of preservation that emphasizes sustainability and effectiveness while not compromising consumer trust.
The most common approach to product protection today involves the use of antimicrobial agents, which can be synthetic, naturally derived, or combined with multifunctional ingredients. While preservatives are often considered a relatively modern development from the latter half of the 20th century, their use dates back thousands of years. Ancient Egyptians, known for their advanced cosmetic practices, incorporated copper sulfate in their eyeshadows — an early example of a preservative (5).
Today’s preservatives for cosmetic and personal care products are far more sophisticated and effective. Regulatory frameworks like the EU’s Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 ensure the safe use of preservatives, allowing small quantities to protect large volumes of products over extended periods. Current validation of preservation systems requires adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP), raw material quality control, and verification of preservative efficacy through methodologies like the challenge test (6).
Preservatives approved by regulatory bodies include parabens, isothiazolinones, organic acids, formaldehyde releasers, or halogenated compounds such as triclosan and chlorhexidine — each with distinct antimicrobial mechanisms depending on their chemical structure and functional groups (7). Product degradation can result from microbial contamination or exposure to atmospheric oxygen. To prevent this, two main categories of protecting agents are used: antimicrobial preservatives, which inhibit microbial growth, and antioxidants, which prevent oxidation and the formation of free radicals (8).
Among the preservatives, parabens remain widely used due to their effectiveness against a broad spectrum of bacteria and fungi and their stability across a wide pH range. However, their use has sparked controversy due to concerns about their potential estrogenic activity, prompting a growing interest in safer and more sustainable alternatives. In response, natural preservatives offer a promising alternative, providing effective protection against fungi and bacteria while supporting safety claims.
Multifunctional ingredients
The introduction of multifunctional ingredients in cosmetics marked a significant advancement in preservation and formulation strategies. In the early 1990s, the first multifunctional ingredients began to emerge, offering benefits beyond product protection. Among most common ingredients that can be used as product protectors with additional skin care benefits are Pentylene Glycol, Caprylyl Glycol, 1,2-Hexanediol, Ethylhexylglycerin, Glyceryl Caprylate, and some others (9).
These so-called 1,2-alkanediols, with carbon chain lengths ranging from C5 to C10, are often used alongside other chemically distinct compounds such as hydroxyacetophenone or naturally derived alcohols like phenylpropanol. All these substances quickly gained attention for their ability to provide multiple benefits, such as moisturizing, stabilizing, and enhancing product texture, while also contributing to microbial protection(10). Their versatility and generally favourable safety profiles made them an appealing alternative to traditional preservatives.
Several studies have reported that 1,2-alkanediols show increasing anti-microbial activity as their alkane chain length increases (11). 1,2-Alkanediols such as 1,2-pentanediol (C5), 1,2-hexanediol (C6), or 1,2-octanediol (C8) are frequently used in cosmetic applications because of their excellent moisturizing properties, emollient properties, and effectiveness as a solvent. Additionally, these aliphatic 1,2-diols possess anti-microbial activity (12).
While 1,2-alkanediols rarely occur in nature (13), advancements in technology now enable their production through biofermentation and green chemistry processes. These naturally derived ingredients help formulators reduce preservative levels or provide broad-spectrum natural protection in appropriate applications (14).
Today, natural antimicrobial systems in cosmetic formulations must meet several key criteria (15):
- Effectiveness: Delivering reliable protection.
- Compatibility: Working seamlessly with other formula ingredients.
- Safety: Gentle and non-irritating for the skin.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting global safety standards.
- Sustainability: Sourced responsibly and renewably.
Though multifunctional ingredients may require careful combination for broad-spectrum protection, they offer a flexible approach for creating the perfect balance of safety and performance.
Sustainability uncompromised
Sustainability stands out as the predominant trend in the beauty industry. It continues to be a key focus area within the ingredient sector, encompassing initiatives to conserve resources, increase efficiency, and reduce waste.
As brands seek simplified INCI lists, formulators prioritize efficiency, and the industry aims to cut costs, the demand for multifunctional ingredients has never been higher. The study (16) from Kline’s Elodie Alves highlights that multifunctionality in beauty goes beyond just consumer-facing trends. While hybrid products like makeup-skincare hybrids, whole-body deodorants, and combined hair and scalp treatments are gaining popularity, the impact of multifunctionality is increasingly evident in ingredient lists. This shift is driven by the need to save time and reduce costs in personal care, amplified by rising ingredient prices due to high labor and energy expenses. As a result, suppliers and formulators are exploring new benefits of existing ingredients to streamline formulations and develop multifunctional products. Additionally, simplified ingredient lists enhance consumer understanding and trust, while the push for minimalism aligns with sustainability goals by conserving resources and reducing product waste (17).
Moreover, this reduction in formulation complexity makes it easier for brands to achieve transparent labeling and meet the growing demand for sustainable and effective beauty products.
The future of preservation in rebuilding consumer trust
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, sustainability in beauty is no longer optional; it's a baseline expectation (18).
However, “the clean beauty” movement is facing growing consumer confusion and distrust, largely due to unclear and unsubstantiated environmental claims. Although over half of UK beauty product launches in early 2023 featured ethical and environmental claims, 65% of adults struggle to determine whether brands exaggerate their eco-friendliness (19). EU legislation is intensifying efforts to combat misleading environmental claims, commonly known as greenwashing, by introducing new regulations to enhance transparency. The European Commission has proposed a law on green claims, aiming to ensure that environmental labels and claims are credible and trustworthy, thereby enabling consumers to make better-informed purchasing decisions (20).
Safety concerns further challenge the growth of clean beauty movement. According to a recent Mintel report, 80% of beauty and personal care consumers advocate for tougher safety standards, reflecting widespread scepticism toward new ingredients (21). This concern extends to ingredient safety, sourcing, production transparency, and the credibility of product claims. Moreover, 37% of beauty and personal care users are influenced by scientific research on ingredients, while 44% of clean beauty consumers see clinical studies as a key pillar of trust (22).
To rebuild this trust, brands must prioritize ingredient transparency, provide clear sustainability data across a product’s lifecycle, and offer accessible tools that empower consumers to make informed choices. At the same time, ongoing innovation in preservation strategies is creating smarter solutions that balance antimicrobial protection, efficacy, and consumer demand for naturalness and sustainability. What was once considered exclusive to the premium segment is now becoming accessible across all cosmetic categories — from mass market to luxury — making sustainable ingredient solutions affordable and available to every consumer. This democratization of high-performance, eco-friendly ingredients marks a significant step toward a more inclusive and responsible beauty industry.
Conclusion
The future of cosmetics lies in the continued evolution of holistic approaches which represents a transformative shift in the industry, merging scientific advancements, natural ingredients, and wellness principles. By understanding and embracing the interconnectedness of these elements, the cosmetics industry can cultivate products that not only enhance external beauty but also contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and the planet.
The interplay between beauty from within and topical cosmetics is the key for future products. The integration of biotechnology and green chemistry is revolutionizing cosmetic formulations, offering sustainable and biocompatible alternatives.
Developers can implement blockchain to trace the journey of ingredients from source to product. Nevertheless, the efficacy of the natural products should be scientifically proven. Marketers can communicate transparency as a brand value, and parallelly educate consumers by highlighting how specific ingredients contribute to radiant and healthy skin.
By embracing the synergy between these approaches and leveraging scientific advancements, the cosmetics industry can provide consumers with comprehensive beauty solutions that cater to both internal and external dimensions of beauty.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
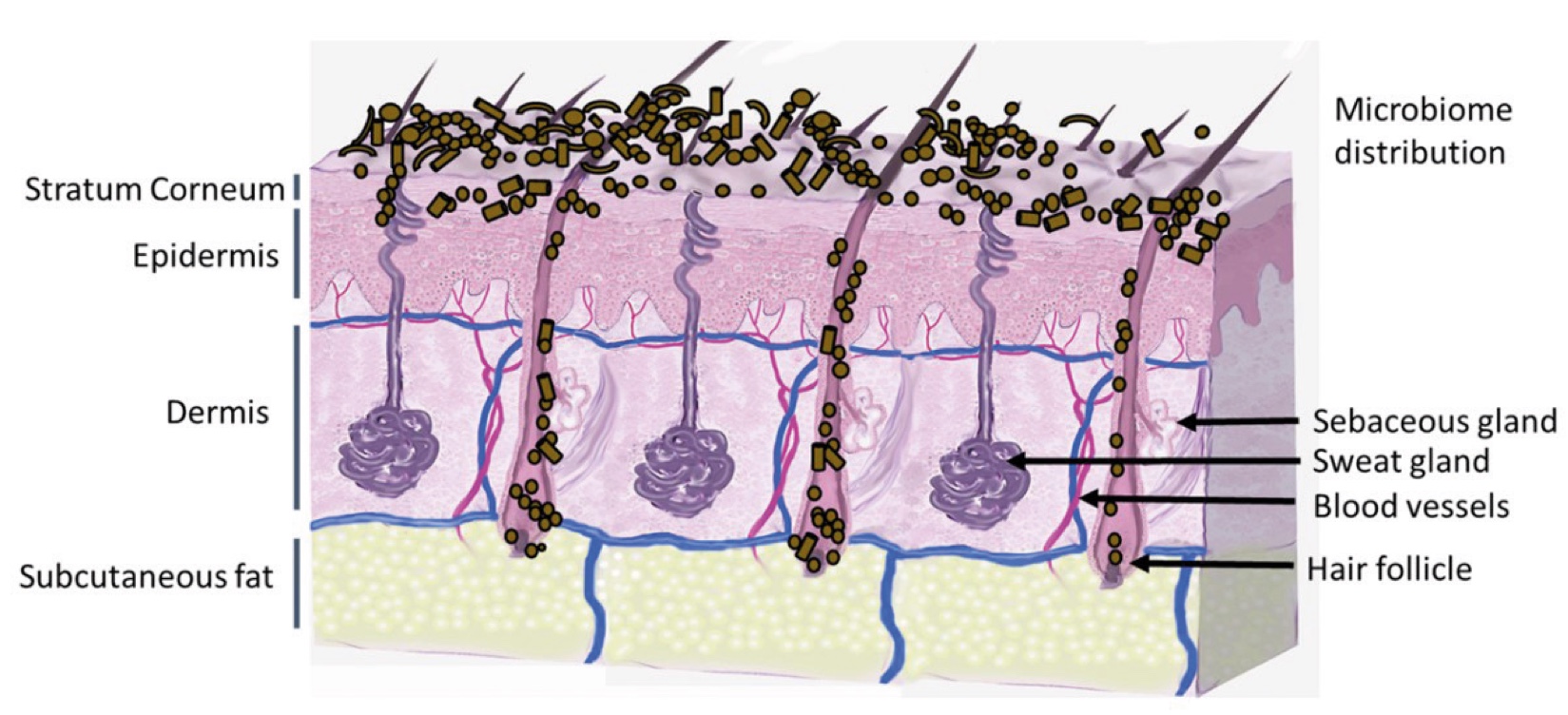
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- Euromonitor International, Passport Sustainability: Consumer trends and industry insights 2025: https://go.euromonitor.com/webinar-2025-consumer-trends-and-industry-insights.html
- Euromonitor International, Consumer trends to watch, 2024. https://go.euromonitor.com/webinar-2024-consumer-trends-to-watch.html
- Global Market Insights, Cosmetic Preservatives market, https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/cosmetics-preservative-market
- Ibid.
- Cosmetics Europe: Fact sheet preservatives, https://cosmeticseurope.eu/files/2315/5246/7405/CE_Factsheet_preservatives_March_2019.pdf
- National Center for Biotechnology Information, Cosmetics Preservation: A Review on Present Strategies, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6099538/
- ibid.
- ibid.
- Balint Koroskenyi, Modern product protection 2.0, Eurocosmetics, https://www.eurocosmetics-mag.com/modern-product-protection-2-0-green-multifunctionals/
- ibid.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information, The influence of alkane chain length on the skin irritation potential of 1,2-alkanediols - PubMed, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21585401/#:~:text=Like%20anti%2Dmicrobial%20activity%2C%20sensory,of%201%2C2%2Dalkanediols.
- ibid.
- M. J. Klug, A. J. Markovetz, Journal of Bacteriology 1967, Vol. 93, No. 6, 1847-1852, https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.93.6.1847-1852.1967
- Dr. Barbara Olioso, The Ultimate Guide to Cosmetic Preservative Selection, SpecialChem:https://cosmetics.specialchem.com/selection-guide/preservatives-for-cosmetic-formulations
- ibid.
- KLINE + Company, Why is Multi-Functionality Demand Rising in the Personal Care Industry?, https://klinegroup.com/chemicals/why-is-multi-functionality-demand-rising-in-the-personal-care-industry/
- KLINE + Company, Personal Care Ingredients: Global Market Analysis, 2024. https://klinegroup.com/chemicals/pci-market-update-trends-shaping-the-future/
- Mintel, Trend: Sub-Zero Waste, 2019: https://clients.mintel.com/content/trend/2019-trend-sub-zero-waste
- Mintel, Conscious Cosmetics: The Rise of Clean Beauty, 2025: https://www.mintel.com/insights/beauty-and-personal-care/conscious-cosmetics-the-rise-of-clean-beauty/
- European Commission, Green Claims: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/circular-economy/green-claims_en?utm_source=chatgpt.com
- Mintel, https://www.cosmeticsdesign.com/Article/2025/02/19/mintel-80-of-consumers-want-stricter-safety-regulations-in-beauty/
- Ibid.
