
Formulation
Skin care
peer-reviewed
The feel of foam: innovating sensory evaluation for solid shampoo formulations
AMELIE DORMOY1*, NICOLAS ENTREMONT1, LOUISE TREINT1, SARAH BOUZRAA1, ANNE-MARIE PENSE-LHERITIER2, FRANÇOIS BOUTON1
1. BRENNTAG, Lesquin, France
2. FRM GaleSens, Cergy, France
*Corresponding author
ABSTRACT: The solid cosmetic market, especially for shampoos, is growing due to consumer demand for sustainable, waterless, and plastic-free products. Key surfactants include Sodium Cocoyl Isethionate (SCI), Sodium Coco Sulfate (SCS), and Alkylpolyglucosides (APG), chosen for their mildness and performance. Sensory aspects—particularly foam volume, texture, and ease of rinsing—are critical for consumer satisfaction. A study of European solid shampoos led to a standardized sensory evaluation protocol using hair strands. This method evaluates key sensory attributes such as foam homogeneity, bubble size, and cushion effect. Using a consensus profiling approach, it enabled an effective comparison of four solid shampoo formulations. This article seeks to introduce a standardized protocol for evaluating foaming solid cosmetics, enabling a systematic assessment of new surfactants and formulation approaches. The ultimate aim is to enhance product performance while effectively meeting consumer sensory expectations.
??????????????????
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”
Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
Introduction
The solid cosmetics market, especially in hygiene and hair care, is steadily expanding, driven by consumer demand for sustainability, reduced plastic use, and minimalist formulations (1) In 2024, the global solid shampoo segment was estimated at $11–15 billion, with an average annual growth rate between 5.6% and 7.7% (2, 3). Mintel also reports a sharp increase in bar/solid product launches since 2020, with sustained interest from 2023 onward (4). These formats are now seen as credible eco-conscious alternatives, especially in natural, niche, or direct-to-consumer channels.
On the formulation side, MyKline (5) data highlights that acyl isethionates, primarily SCI, are leading anionic surfactants. APGs are also widely used for their mildness and biodegradability. SCS remains a key secondary surfactant in solid hair care formats. As solid formats continue to evolve in both composition and positioning, sensory performance has emerged as a central driver of consumer acceptance.
Among the critical sensory attributes of solid foaming products, foam remains a pivotal factor. It is often linked to perceptions of cleanliness and efficacy, despite this association being more psychological than scientifically substantiated. Additionally, foam contributes significantly to user satisfaction; a creamy and dense lather enriches the overall sensory experience. The product must also feel pleasant in hand and spread easily through hair (6).
Formulation challenges of solid shampoos
Formulating solid shampoos presents unique technical challenges. The bar should be hard enough to resist melting when used and especially not break after multiple uses. The hardness of a solid bar is obtained by mixing natural waxes, butters, and fatty alcohols. Cetyl alcohol or cetearyl alcohol are the most common fatty alcohols used to achieve the desired hardness, while shea or cocoa butter are commonly used natural butters. Kaolin clay and other natural powders may be included for their oil-absorbing and scalp-purifying benefits, especially in products targeting oily hair or scalp conditions.
Due to this oil-rich base, powdered surfactants like SCS and SCI are preferred (7). APGs, typically available in liquid form, are valued for their mildness and biodegradability (8). However, their water content can complicate incorporation into solid bars and pose preservation challenges. The development of solid or powder-form APGs would be highly advantageous, enabling easier formulation and improved stability. Reliable sensory evaluation methods are also needed to assess their performance in solid shampoo formulations and would greatly support product development and optimization.
Case study: development of a protocol using hair strands
The objective of this study was to develop a reliable protocol for evaluating the sensory qualities of foam in solid shampoos, including the impact of a new powdered decyl glucoside. To achieve this, a systematic approach was followed, beginning with the selection of representative solid shampoo products to serve as examples. Sensory descriptors relevant to foam performance were then defined, enabling a structured evaluation framework. The panel conducted consensus-based evaluation to generate detailed sensory profiles.
Selection of representative solid shampoo products
Around 20 solid products available on the European market were selected. Among these:
- 30% used a Sodium Coco Sulfate (SCS) base
- 20% used a Sodium Cocoyl Isethionate (SCI) base
- 20% used a SCI + decyl glucoside (APG) base
- 30% used other surfactants, alone or in combination
These shampoos exhibited wide diversity in visual appearance, ranging in color and gloss, as well as in texture, with noticeable variations in roughness and hardness. This variability highlights the broad formulation spectrum.
Sensory descriptors relevant to foam performance
To define the appropriate descriptors, the team based their approach on consumer gestures when using solid shampoos, which typically involved holding the bar between the hands to create foam before applying it to the hair.
Hand gesture
The foam evaluation on hands begins by activating the solid shampoo previously dipped in hot water through 10 rotations between wet hands. This method ensures consistent foam generation for sensory assessment. The following key attributes are then rated to characterize the foam quality:
- Hand coverage: How uniformly the foam creates a white layer over the hands; a more uniform white effect corresponds to a higher rating.
- Bubble size: Larger bubbles receive higher scores, reflecting specific sensory preferences.
- Foam homogeneity: The uniformity in bubble size throughout the foam; greater uniformity indicates better foam quality. (Figure 1-1)
Strand gesture
Table 1 below presents the key sensory foam attributes of solid shampoos along with their definitions and standardized protocols for evaluation on hair strands.
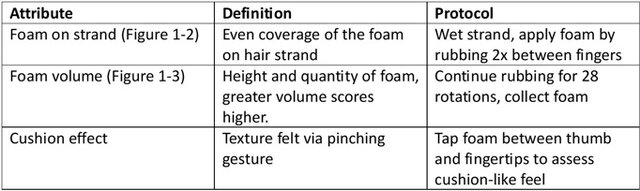
Table 1. Sensory foam attributes on strands

Figure 1. Foam homogeneity (1), strand coverage (2) foam volume (3)
Sensory profile of four formulations
A consensus profile was developed with six participants. In consensus methods, assessors evaluate the products individually and then discuss the attributes and intensities to reach a shared assessment (9) Four products were studied: three currently on the market (A,B,C) and one product under development D:
- Product A: SCS-based
- Product B: SCI-based
- Product C: SCI + decyl glucoside (liquid APG)
- Product D: SCI + solid decyl glucoside (powdered APG)
The results are presented in Figure 2. The developed protocol enables to observe clear differences between the products across all descriptors, except for the cushion effect, which remains a challenging attribute to evaluate. The product A based on SCS and shea butter showed the lowest performance in terms of foam quality. In contrast, the solid APG-based product D, despite being a first, non-optimized formulation, already produced a homogeneous foam
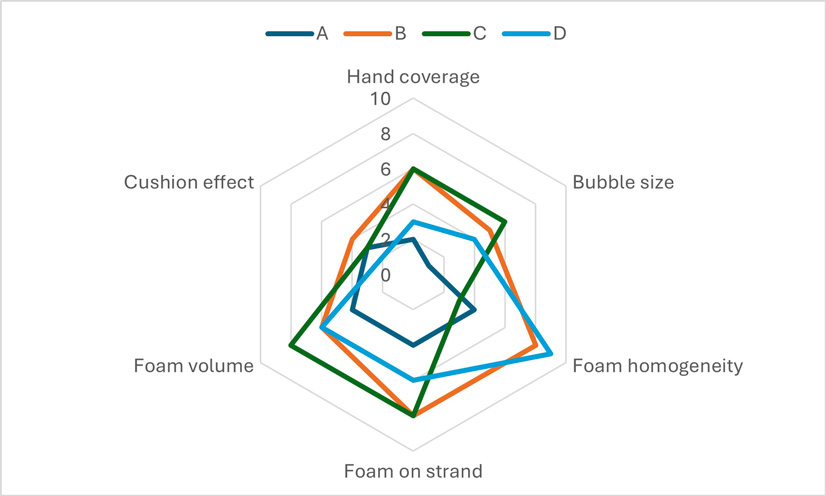
Figure 2. Consensus sensory profile of foam performance
Limits and opportunities for the solid forms
Many surfactants contain water, which complicates waterless formulation. Powdered surfactants are rare, limiting formulation flexibility. However, spray-dried decylglucoside, as studied here, appears promising due to its dry form, mildness and performance.
In 2018, the team had already developed a framework for evaluating liquid shampoos and conditioners (10). However, a specific protocol for bar hygiene products was missing. The sensory evaluation method developed proved effective in distinguishing formulations. It provides a structured, objective way to evaluate full sensory experience from visual appearance to post-rinse feel. This approach supports future innovation in waterless formats by informing improvements in foam, texture and consumer perception.
Conclusion
The development of a straightforward and standardized method for evaluating foam in solid shampoos represents a significant advancement for the cosmetic industry. By clearly defining essential criteria such as foam coverage, bubble size, homogeneity, and cushion effect, this method enables effective comparison across various formulations. This study introduces a practical sensory evaluation protocol tailored for solid shampoos, using the consensus profile method. This approach allows for reliable assessments with a limited number of trained panelists and does not require statistical analysis, making it efficient and reproducible. By clearly defining key sensory attributes, the method enabled the identification of performance differences between formulations, particularly those using spray-dried alkylpolyglucosides. These solid surfactants show strong potential to support the development of mild, effective, and sustainable waterless products. The protocol also provides a foundation for future research on innovative ingredients and formulation strategies adapted to solid formats.
Conclusion
The future of cosmetics lies in the continued evolution of holistic approaches which represents a transformative shift in the industry, merging scientific advancements, natural ingredients, and wellness principles. By understanding and embracing the interconnectedness of these elements, the cosmetics industry can cultivate products that not only enhance external beauty but also contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and the planet.
The interplay between beauty from within and topical cosmetics is the key for future products. The integration of biotechnology and green chemistry is revolutionizing cosmetic formulations, offering sustainable and biocompatible alternatives.
Developers can implement blockchain to trace the journey of ingredients from source to product. Nevertheless, the efficacy of the natural products should be scientifically proven. Marketers can communicate transparency as a brand value, and parallelly educate consumers by highlighting how specific ingredients contribute to radiant and healthy skin.
By embracing the synergy between these approaches and leveraging scientific advancements, the cosmetics industry can provide consumers with comprehensive beauty solutions that cater to both internal and external dimensions of beauty.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
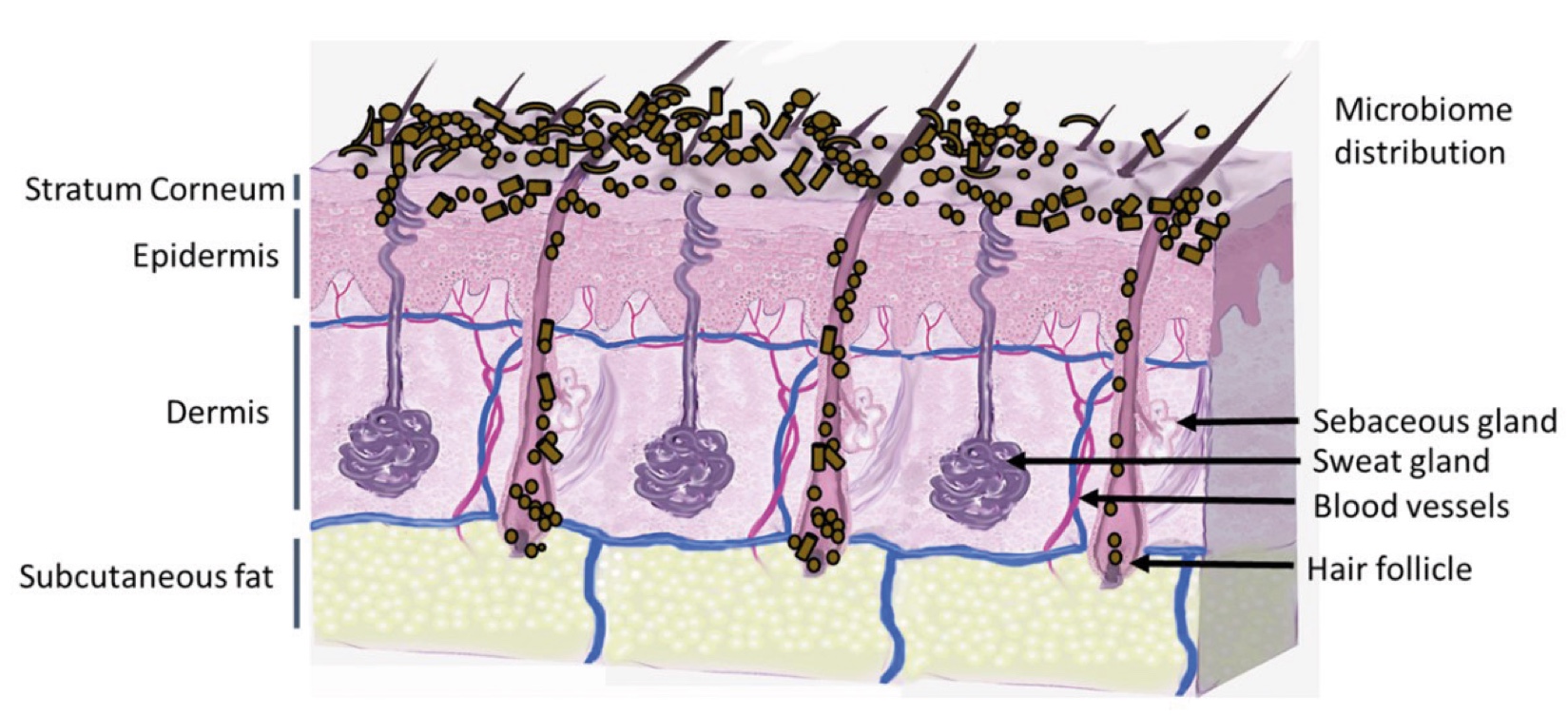
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
1. Gubitosa J, Rizzi V, Fini P, Cosma P. Hair Care Cosmetics: From Traditional Shampoo to Solid Clay and Herbal Shampoo, A Review. Cosmetics 2019, Vol 6, Page 13 [Internet]. 2019 Feb 19 [cited 2025 Jun 24];6(1):13. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/6/1/13/htm
2. Fortune Business Insights. (2025, June 23). Shampoo Bar Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, by Hair Type... Forecast 2025 2032-https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/shampoo-bar-market-108594
3. Proficient Market Insights (on behalf of Business Research Insights). (2025, June 29). Shampoo Bar Market Overview. from https://www.proficientmarketinsights.com/market-reports/shampoo-bar-market-2754
4 Mintel. (2021, September 23). Raising the bar: Building a solid future for beauty formats., from https://www.mintel.com/insights/beauty-and-personal-care/raising-the-bar-building-a-solid-future-for-beauty-formats
5 MyKline. (2023, November 13). Top Trends Shaping the Future of Hair Care Ingredients from https://klinegroup.com/chemicals/top-trends-shaping-the-future-of-hair-care-ingredients
6 Cornwell PA. A review of shampoo surfactant technology: consumer benefits, raw materials and recent developments. Int J Cosmet Sci . 2018 ;40(1):16–30. Available from: /doi/pdf/10.1111/ics.12439
7 J N, M A, Priya K D, Kumar M N. Formulation and Evaluation of Naturally Derived Shampoo Bar. Int J Innov Sci Res Technol [Internet]. 2025 Apr 18 [cited 2025 Jul 3];481–7. Available from: https://www.ijisrt.com/formulation-and-evaluation-of-naturally-derived-shampoo-bar
8. Alkyl Polyglucosides in Haircare – How to Use APGs in Solid Shampoo Bars Available from: https://swonlab.com/alkyl-polyglucosides-solid-shampoo-bars/
9. International Organization for Standardization. (2016). ISO 13299:2016 — Sensory analysis — Methodology — General guidance for establishing a sensory profile. ISO. https://www.iso.org/standard/63553.html
10 Roux, J.-B., Bouton, F., Bauer, C. F., Pavanelli, A., Lavarde, M., & Pensé-Lhéritier, A.-M. (2018, October). Sensory assessment of shampoo containing new conditioner in comparison with shampoos containing silicone. [Conference presentation]. IFSCC 2018, Munich, Germany. Retrieved from from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328476944_SENSORY_ASSESSMENT_OF_SHAMPOO_CONTAINING_NEW_CONDITIONNER_IN_COMPARISON_WITH_SHAMPOOS_CONTAINING_SILICONE
