
Multifunctional Ingredients
Skin care
KEYWORDS
HYDROXYACETOPHENONE;
MULTIFUNCTIONAL;
ANTIOXIDANT;
PRODUCT PROTECTION.
PLANT INGREDIENTS,
SUSTAINABLE,
GREEN BIOACTIVES.
peer-reviewed
A multifunctional ingredient with diverse benefits: Hydroxyacetophenone
Balint Koroskenyi, Ph.D.
Symrise, USA
ABSTRACT: In the dynamic and demanding landscape of product development, formulators increasingly seek ingredients that streamline their efforts while delivering diverse consumer benefits. 4-Hydroxyacetophenone (HAP, INCI: Hydroxyacetophenone) has emerged as a particularly promising multifunctional agent, offering an unparalleled combination of properties suitable for a wide range of personal care applications. This review discusses HAP's diverse functionalities, robust safety profile, and formulation versatility. Additional, formerly unpublished, data is also presented to further illustrate the functionalities.
Studies confirm HAP's potent antioxidant activity, demonstrated both in vitro and ex vivo. Its notable soothing properties effectively mitigate skin irritation and align with the growing consumer demand for sensitive skin solutions. Furthermore, HAP supports robust broad-spectrum product protection at low use levels when combined with conventional antimicrobials. Extensive safety assessments affirm its benign status, combined with skin microbiome-friendly attributes.
??????????????????
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”
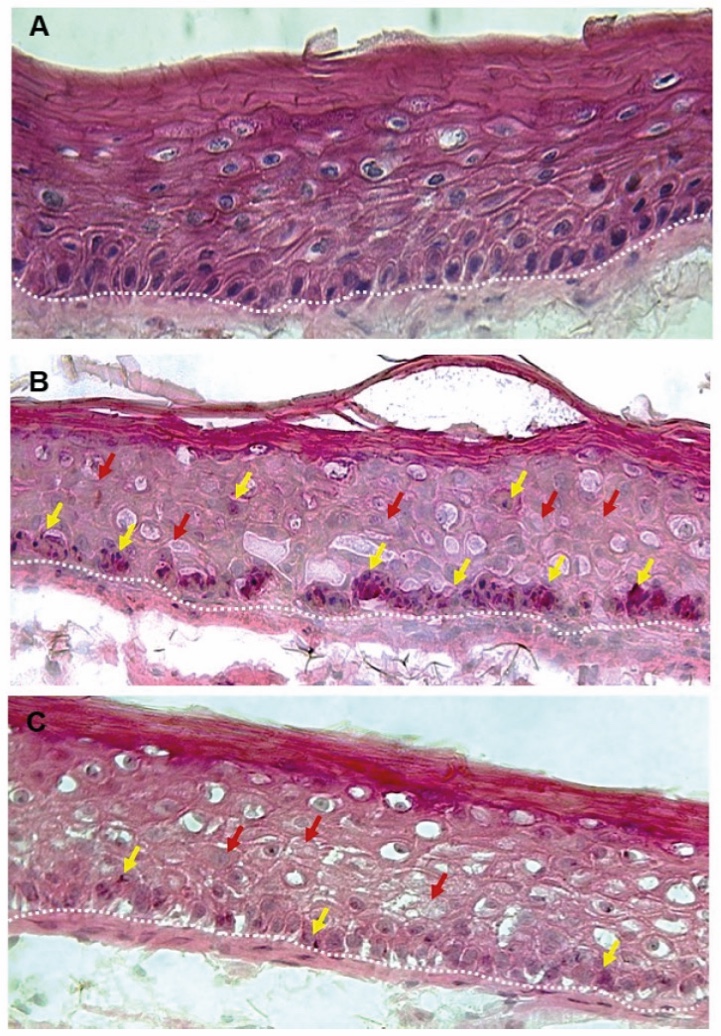
Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
Introduction
Today’s formulators have a multitude of options for building successful formulations that cater to a diversity of consumers with varying demands, desires and priorities. One can reduce formulation complexity and accelerate development time by using multifunctional ingredients that can deliver several benefits simultaneously. Some multifunctionals offer more functions and are better at achieving the desired benefits than others. No other multifunctional has been quite as successful in demonstrating real, sought-after benefits at a power even surpassing single-function, dedicated ingredients than Hydroxyacetophenone. Since its discovery in 2013 by Symrise, the industry has learned a lot about the true capabilities of this cosmetic ingredient.
4-Hydroxyacetophenone was introduced to the cosmetic market in 2013. This aromatic ketone, also known as p-Hydroxyacetophenone or piceol, occurs naturally in an herb native to Latin America, Lampaya hieronymi (1), in an edible fruit-bearing flowering plant of the rose family native to Alpine and arctic regions, cloudberry, and in Norway Spruce (2). In fact, Hydroxyacetophenone is GRAS listed. In its pure form, it’s a white to beige crystalline powder with water solubility up to its highest recommended use level, 1%. The ingredient is stable at least up to 100oC. In addition to the solid form of the neat material, Hydroxyacetophenone is also available in liquid preservative or multifunctional blends (3).
In this paper, we are reviewing the key aspects of this ingredient including its main cosmetic benefits, how to formulate with it, and its safety profile. We are also introducing new experimental data on its antioxidant properties via an in vitro ABTS assay and an ex vivo scalp study, as well as on its product protection enhancing performance.
Materials and Methods
ABTS assay:
The assay principle is based on the reductive decolorization of the green colored cationic radical 2,2’-Azinobis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline 6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS·+) by antioxidants (4). The decolorization can be measured spectrophotometrically at 734 nm. Determination of the antioxidant capacity was performed in 96-well microplates from Nunc (Wiesbaden, Germany) and with the microplate reader “Spark” from Tecan (Crailsheim, Germany). The test sample was diluted to 5 different concentrations (0.0068%, 0.0034%, 0.00068%, 0.00028%, 0.00006%). 20 ml of each test sample, solvent (control), and 200 ml of the background control were pipetted into separate wells of a 96-well plate. 180 µl of the potassium persulfated oxidized ABTS+ - usage-solution was added to the wells with samples, blank control and mixed shortly and carefully without bubbles. The plate was incubated at 30oC for 10 min in the dark. Absorption was detected at 734 nm.
Ex vivo scalp study:
Test formulations were prepared with the compositions of Tables 1 and 2:
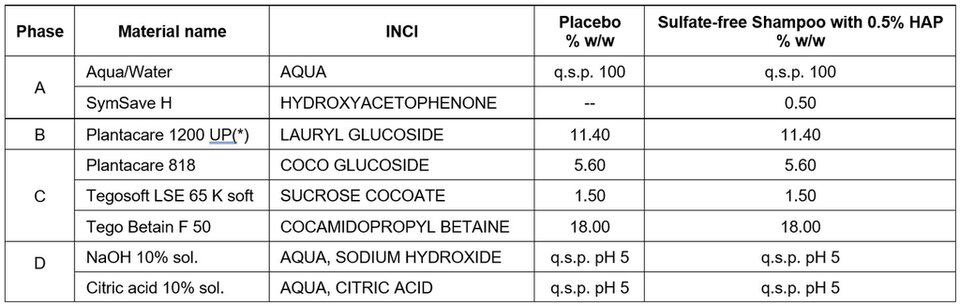
Table 1. Shampoo test formulations for ex vivo scalp study.
- Mix Phase A and stir until homogeneous
- Incorporate Phase B into A and stir until homogeneous
- Incorporate Phase C in the given order and mix until homogeneous
- Adjust the pH with Phase D to approx. pH 5.
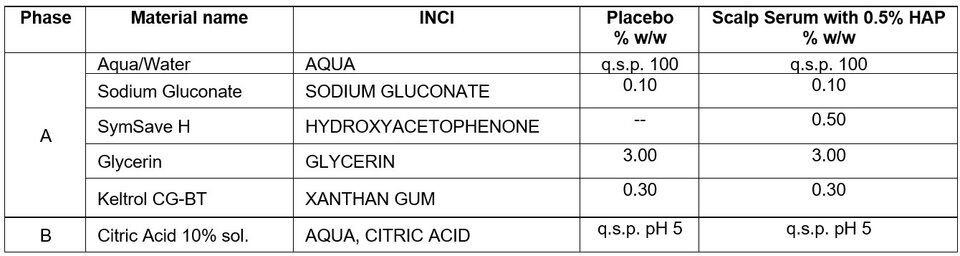
Table 2. Scalp serum test formulations for ex vivo scalp study.
- Mix all ingredients of phase A and heat up to 40°C (when HAP is used)
- Adjust to pH 5 using phase B
Scalp fragments were fractionated into pieces of approximately 1.5 cm2, placed in culture plates (Corning, USA) with specific culture medium and kept in an incubator at 37ºC in the presence of 5% CO2. In the scalp fragments were applied 25-30 mg/cm2 of the shampoo formulations with circular movements, kept in culture for 5 minutes and then rinsed with PBS 1x. After that the fragments were treated with 25-30 mg/cm2 of the serum formulations and were kept in cultures for 2 days.
After incubation, the scalp specimens were subjected to a dose of 15 J/cm2 of ultraviolet (UV) radiation using UVA Cube 400, SOL 500 H1 filter and UV Meter devices (Honle UV America Inc., MA, USA).
An additional application was made. The fragments were kept for another 24 hours with the products evaluated and the fragments were collected for labeling and semi-quantification of free radical synthesis using a DCFH-DA probe. After the treatment period, the scalp fragments were embedded in Tissue-Tek® O.C.T.™ and then serial 12-micrometer histological sections were taken directly onto silanized slides with a cryostat (Leica, GER - CRYOCUT 1800). The sections were then washed with phosphate buffer (PB) and incubated for 1 minute with a solution (1:10,000 in phosphate buffer) of Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA; Sigma, USA).
The fluorescence intensity parameter emitted by the oxidation of the DCFH-DA probe was analyzed under the microscope (OLYMPUS, JAP - BX53) using CellSens software (©2010 OLYMPUS CORPORATION).
After obtaining the images, the fluorescence intensity was quantified using ImageJ software (version 1.48, Arbitrary Units - A.U.).
The statistical evaluation used the ANOVA test to measure the variation in the results, comparing the data between the groups. The Bonferroni post-test was then applied, which reinforced and made the results presented in the ANOVA test even more precise. A 5% significance level was used.
Preservative Efficacy Test (PET):
The challenge tests were carried out in accordance with the European Pharmacopia (Ph. Eur.).
Results and Discussion
Antioxidant properties
Antioxidants are ubiquitous ingredients in cosmetics, present in close to 40% of global personal care product launches (5). They are essential in maintaining the stability of certain unsaturated ingredients, such as some natural oils. They are also used to inhibit or control oxidation in the skin. Many products with anti-ageing claims also contain antioxidants. Their role in maintaining scalp health has also been recognized. Oxidative stress in the scalp may lead to seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff), scalp odor, or even hair loss (6). Antioxidant activity is one of the most useful benefits in cosmetics and is offered by only a very few multifunctionals, such as Hydroxyacetophenone and Tropolone. This property alone is a good reason to incorporate the ingredient in a formulation.
An in vitro ABTS assay demonstrated the strong antioxidant efficacy in comparison with Trolox (6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchroman-2-Carboxylic Acid), a water-soluble analog of vitamin E commonly used in antioxidant capacity studies as a positive control (Figure 1).
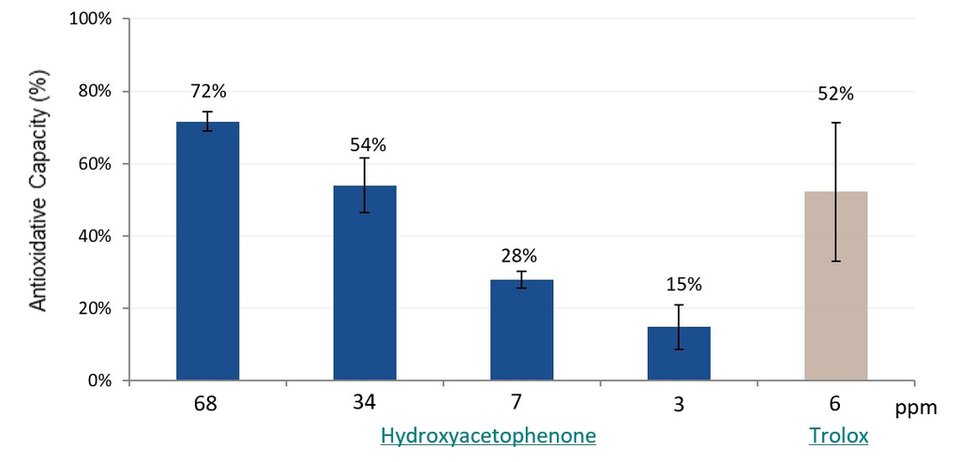
Figure 1.In vitro test results of the antioxidant activity of Hydroxyacetophenone in comparison with the positive control Trolox in an ABTS assay.
Antioxidant activity was further confirmed by an ex vivo study on scalp fragments obtained from surgical procedures, using UV exposure followed by semi-quantification of the oxidative stress via fluorescence measurement (Figure 2).
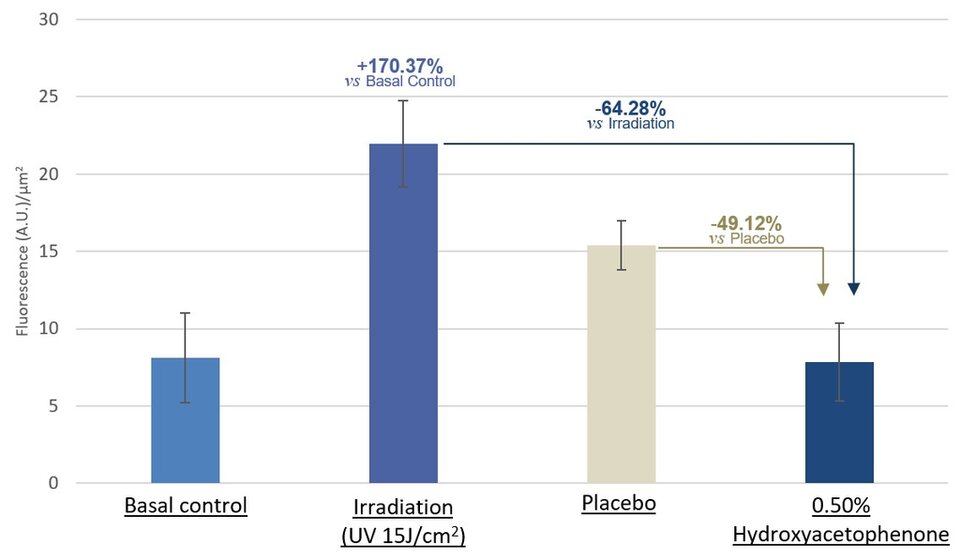
Figure 2. Ex vivo fluorescence data showing the reduction of oxidative stress on scalp fragments when treated with a scalp serum containing 0.50% Hydroxyacetophenone.
Soothing properties
4-Hydroxyacetophenone truly stands out among multifunctional ingredients with its unique properties. One such special feature is its soothing benefit through the inhibition of the COX-2 enzyme (1). This substance helps reduce skin irritation and is therefore an ideal ingredient in nearly any personal care formulation to provide a calming effect. Particularly considering the growing consumer demand for products with sensitive skin claims, such a benefit is more than a curiosity: it’s a need answered.
Product protection performance
The support of broad-spectrum performance elevates the status of Hydroxyacetophenone among multifunctionals. It’s one of the very few options available today to support antifungal protection. Robust performance is seen at low use levels in various formulation types when combined with antimicrobial ingredients. A multitude of combinations have been shown to demonstrate its versatility. A few examples are shown in Figures 3-5.
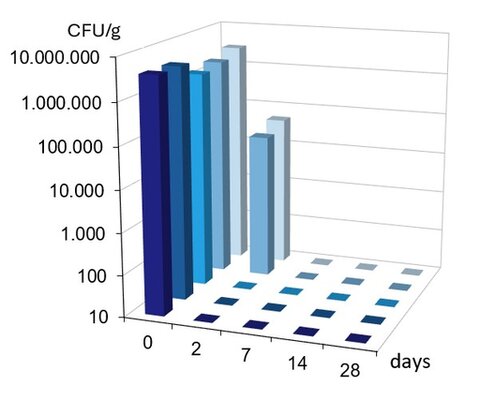
Figure 3. Challenge test results of 0.5% Hydroxyacetophenone + 0.5% Phenoxyethanol in O/W emulsion;
E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, C. albicans, A. brasiliensis
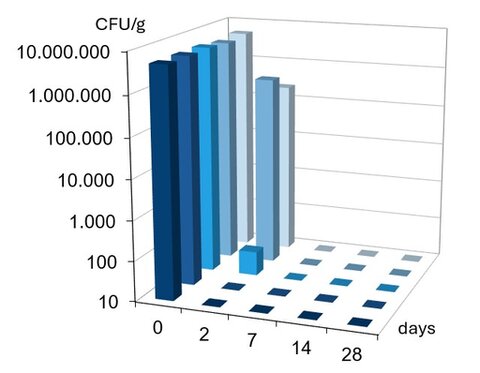
Figure 4. Challenge test results of 0.5% Hydroxyacetophenone + 0.1% o-Cymen-5-ol in O/W anionic emulsion;
E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, C. albicans, A. brasiliensis
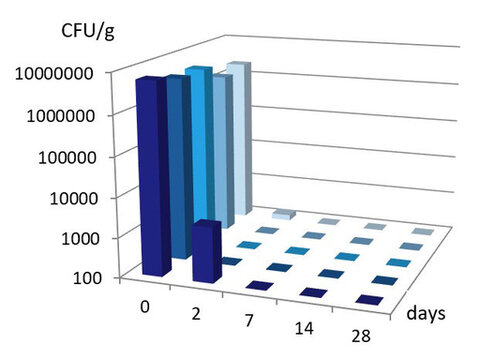
Figure 5. Challenge test results of 0.2% Hydroxyacetophenone + 0.5% Sodium Benzoate in a shampoo formulation; E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, C. albicans, A. brasiliensis
Conclusion
The future of cosmetics lies in the continued evolution of holistic approaches which represents a transformative shift in the industry, merging scientific advancements, natural ingredients, and wellness principles. By understanding and embracing the interconnectedness of these elements, the cosmetics industry can cultivate products that not only enhance external beauty but also contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and the planet.
The interplay between beauty from within and topical cosmetics is the key for future products. The integration of biotechnology and green chemistry is revolutionizing cosmetic formulations, offering sustainable and biocompatible alternatives.
Developers can implement blockchain to trace the journey of ingredients from source to product. Nevertheless, the efficacy of the natural products should be scientifically proven. Marketers can communicate transparency as a brand value, and parallelly educate consumers by highlighting how specific ingredients contribute to radiant and healthy skin.
By embracing the synergy between these approaches and leveraging scientific advancements, the cosmetics industry can provide consumers with comprehensive beauty solutions that cater to both internal and external dimensions of beauty.
The performance can be further optimized by selecting various physical or chemical factors. This is well described in detail in other publications (7, 8).
Formulating
Even though this solid, crystalline substance is soluble in water at its recommended use level of up to 1%, complete dissolution may take about an hour at room temperature, which can be accelerated by gently heating the water phase (50-60oC). Recently, a water-soluble liquid blend was developed to enhance the processability (6). It’s also soluble in a variety of cosmetic ingredients, such as Pentylene Glycol, Propylene Glycol, Dipropylene Glycol, Glycerin, Ethanol, Propanediol, or Caprylic/Capric Triglyceride. The ingredient has good compatibility with a wide variety of formulations. The ketone molecular structure ensures good stability in a broad pH range and at elevated temperatures.
Safety
The safety of 4-Hydroxyacetophenone has been thoroughly reviewed by both the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association (FEMA)(9) and the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) (10). Both authoritatively concluded that the ingredient is safe. In fact, the substance is listed as GRAS (Generally Regarded As Safe) (11). It’s important to note that Hydroxyacetophenone does not cause irritation or sensitization. On the contrary, this known soothing agent actually helps to reduce irritation and inflammation caused by other substances in the formulation by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme involved in irritation and inflammation. In vivo microbiome studies coupled with gene sequencing have shown that the substance does not impact healthy skin microbiome (12).
4-Hydroxyacetophenone, as a ketone, is structurally very different from well-known aromatic cosmetic ingredients, such as parabens, Benzyl Alcohol, Methylbenzyl Alcohol, Phenethyl Alcohol, and Phenylpropanol, which are aromatic esters or aromatic alcohols, respectively. Consequently, many of its properties, including formulation or skin/hair benefits, antimicrobial performance, and safety profile are strikingly different, and any analogy could be misguided. Even the structurally similar acetophenone shows differences in many aspects.
Hydroxyacetophenone is a globally compliant cosmetic ingredient.
Conclusions
It’s not often that an ingredient pops up that delivers much sought-after properties all in one simple molecule. 4-Hydroxyacetophenone offers some of the most important personal care benefits alongside powerful support of broad-spectrum product protection. These features combined with an excellent safety profile represent a formulator’s wish list packed into a nature-identical GRAS ingredient.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
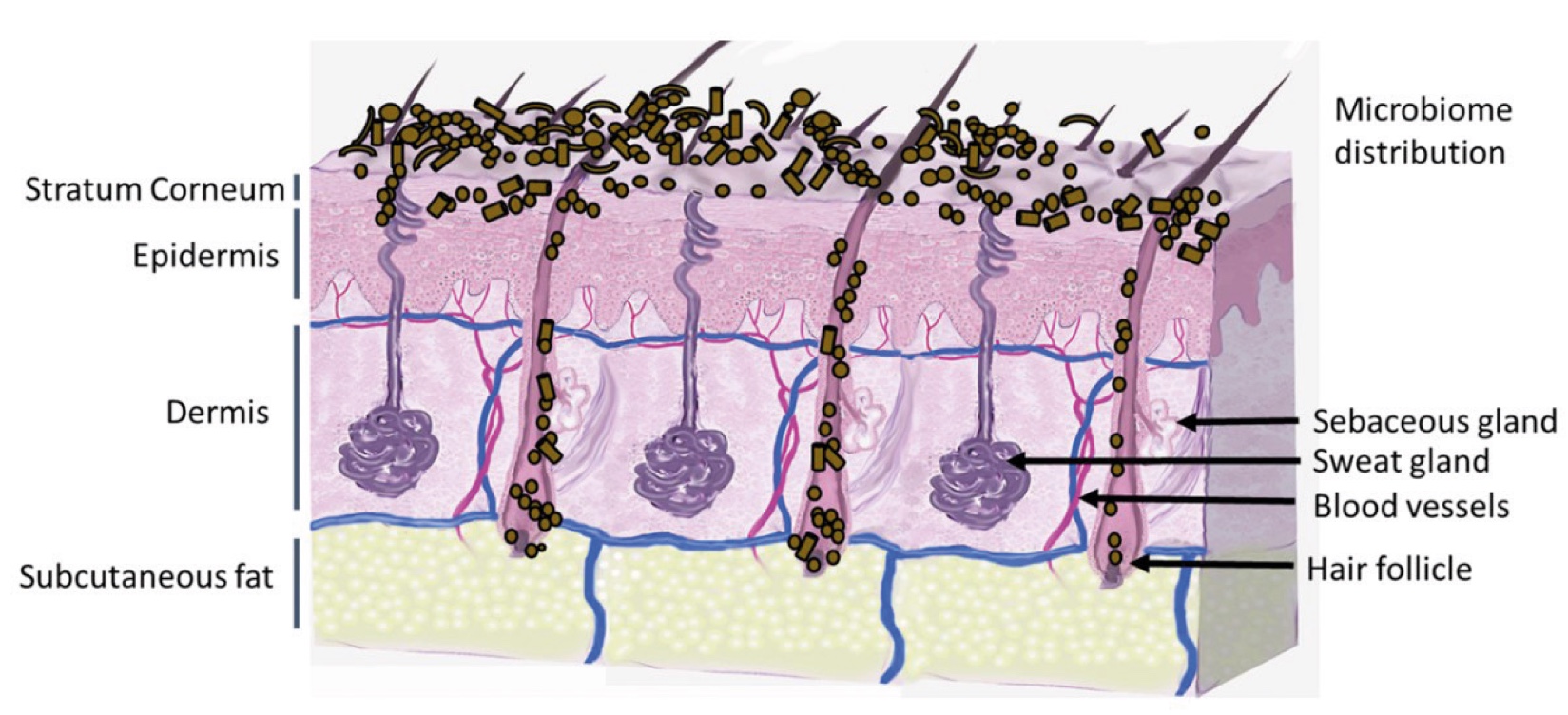
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- Alvarez, M.E., Rotelli, A.E., Pelzer, L.E., Saad, J.R., Giordano, O. Phytochemical study and anti-inflammatory properties of Lampaya hieronymi Schum. ex Moldenke. Il Farmaco 2000; 55(6-7):502-5.
- Metsämuuronen, S., Sirén, H. Bioactive phenolic compounds, metabolism and properties: a review on valuable chemical compounds in Scots pine and Norway spruce. Phytochem Rev. 2019;18(3):623-664.
- Symrise Shapes Water-soluble Liquid Variant of SymSave H: SymSave 5E, Cosmetics & Toiletries, May 7, 2022.
- Re R., Pellegrini N., Proteggente A., Pannala A., Yang M., Rice-Evans C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999;26:1231–1237.
- Mintel
- Davis, MG, Piliang MP, Bergfeld WF, Caterino TL, Fisher BK, Sacha JP, Carr GJ, Moulton LT, Whittenbarger DJ, Schwartz JR. Scalp application of antioxidants improves scalp condition and reduces hair shedding in a 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2021 Nov;43 Suppl 1:S14-S25.
- Koroskenyi, B., Salmen, J., Fontan Yanes, M. T. Multifunctionals Empowered - Part 1, SOFW Journal 12, 2023.
- Koroskenyi, B., Salmen, J., Fontan Yanes, M. T. Multifunctionals Empowered - Part 2, SOFW Journal 06, 2024.
- Adams, T.B., McGowen, M.M., Williams, M.C., Cohen, S.M., Feron, V.J., Goodman, J.I., Marnett, L.J., Munro, I.C., Portoghese, P.S., Smith, R.L., Waddell, W.J., The FEMA GRAS assessment of aromatic substituted secondary alcohols, ketones, and related esters used as flavor ingredients, Food and Chemical Toxicology 2007; 45: 171–201.
- Safety Assessment of Hydroxyacetophenone as Used in Cosmetics, Final Report October 11, 2022, https://www.cir-safety.org/
- FEMA No. 4330
- Exploring Microbiome-friendly Product Protection Solutions, Global Cosmetic Industry, January 22, 2021
