Holistic beauty
on
Skin care

peer-reviewed
Ancient ayurvedic adaptogen ashwagandha - Now trending in modern beauty
BARBARA BROCKWAY
Consultant, United Kingdom
ABSTRACT: Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is an adaptogenic herb that has been used in India's traditional Ayurvedic medicine for over 3000 years. The roots of the ashwagandha plant contain a diverse array of bioactive compounds including withanolides, alkaloids, and antioxidants that are responsible for its rejuvenating and health-promoting properties. Therefore, full spectrum extracts containing these actives at their natural levels provide the greatest benefits. Recent clinical studies have validated ashwagandha's traditional uses for combating stress and for healthy-aging. These studies show ashwagandha is effective for body building along with benefits for skin and hair. Ashwagandha root extract applied topically can improve skin wrinkles, texture, elasticity, and hydration in healthy adults with photo damaged skin. When applied regularly, Ashwagandha root extract can also reduce hair loss, increase thickness and density. Withania somnifera root extract has GRAS status and numerous studies confirm its safety for topical use. The emerging clinical data is adding to ashwagandha's value as a holistic cosmetic ingredient.
??????????????????
Introduction
For over 3000 years ashwagandha, (also called Indian ginseng) has been used to support the mind-body and to help maintain youth, strength and vitality[1]. Ashwagandha promotes outer beauty by caring for the whole body. The holistic properties of this adaptogenic herb make it the perfect ingredient for today's natural beauty products and especially for those taking a wellness-based, inside-out approach to skincare and hair care.
Despite the thousands of years of use, Ashwagandha is new to many people outside of India and its neighbouring countries. However, a burst of pharmacological studies that took place around 2015, has triggered a surge of Worldwide interest in ashwagandha. Unsurprisingly, most interest is still in India and its neighbouring countries, however, as judged by the growing use of ashwagandha as a search term on Google Trends, there is significant interest building in North America, Brazil, Europe, Scandinavia, Australia and parts of Africa (Figure 1).
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”
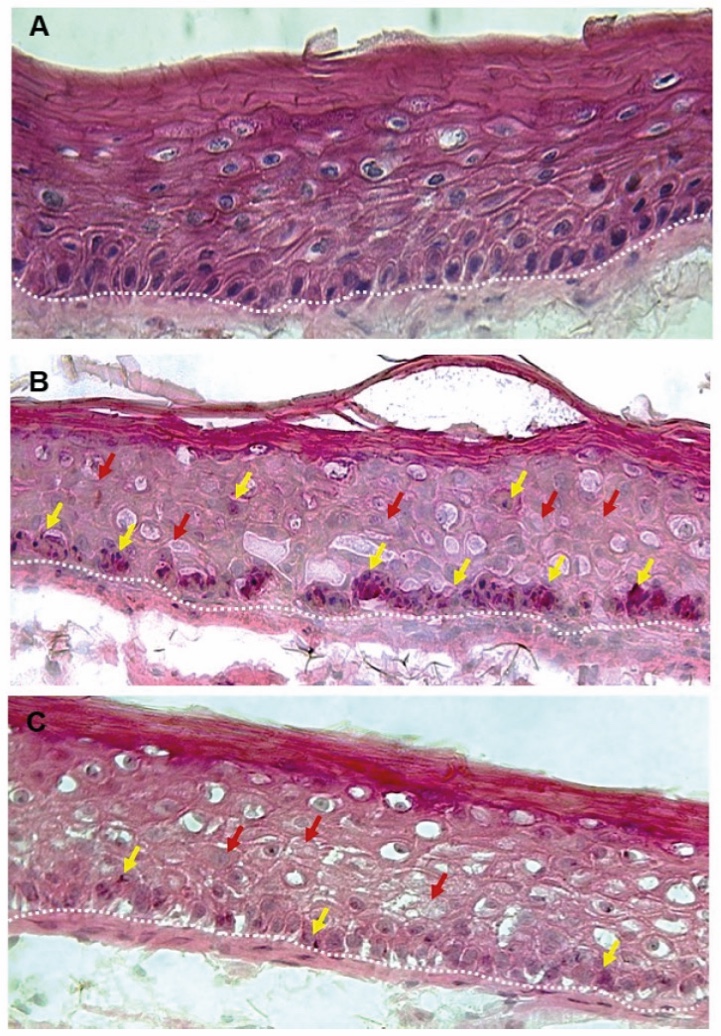
Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
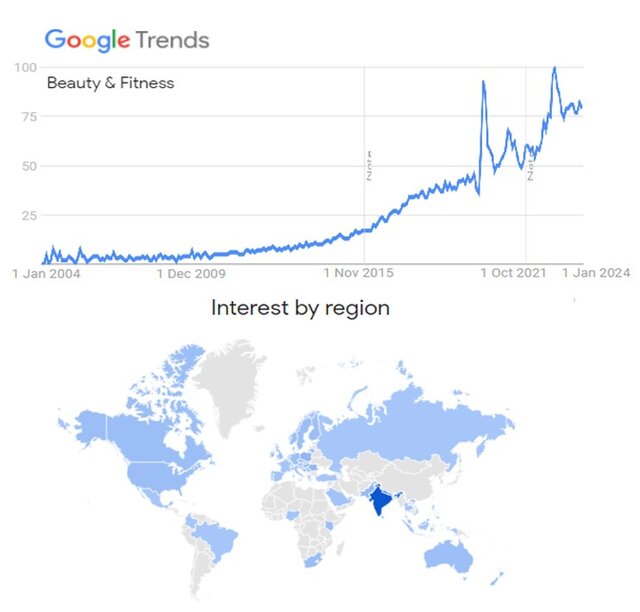
Figure 1. Worldwide growing interest in Ashwagandha, in the beauty and fitness category.
Ashwagandha Botanical Overview
The ashwagandha plant is a small, woody shrub that grows to above 50 cm and can be 2.5 m tall. It is native to the drier regions of India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh. The plant thrives in relatively dry sub-tropical regions with little rainfall and prefers warmer temperatures between 20°C to 35°C without frosts[2]. The cleaned dried roots, ready for processing are shown in figure 2.

Figure 2. Ashwagandha Root, cleaned ready for processing.
Ashwagandha, along with tomatoes and peppers, belongs in the Solanaceae family. Solanaceae is derived from the Latin word solari meaning "to soothe" or "comfort". Ashwagandha is in the genus Withania, and the species is somnifera (meaning "sleep" in Latin) making its scientific name Withania somnifera and the INCI name of the root extract is Withania Somnifera Root Extract, Cas. No. 90147-43-6, EC No. 290-434-9[3].
Ashwagandha Root extracts and not extracts from the leaves or stems
As with all botanical extracts it is important to only use the appropriate part of the plant. When formulating cosmetics, it is only the ashwagandha root that is approved for use by the Government of India, Ministry of AYUSH (Drug Policy Section). Ashwagandha constituents and activities recorded in the major pharmacopoeias such as the United States Pharmacopoeia, the British Pharmacopoeia, the Indian Pharmacopoeia, the Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India, Indian Materia Medica, the Health Canada monograph and the W.H.O. monograph refer exclusively to ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root. Therefore, to be sure of cosmetics regulatory approval and, the chemical composition and efficacy of the cosmetic ashwagandha ingredient, it is important to be sure the ingredient is derived only from ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root.
Benefits of Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is known as "the prince of Ayurvedic herbs" and is used to promote wellbeing and for its youth-preserving and health-promoting properties. It has a leading role in Rasayana, the branch of Ayurveda which focusses on rejuvenation, longevity, and healthy-aging. The term Rasayana means "path of essence," implying nourishment and Rasayana therapies aim at promoting tissue renewal, mental clarity, happiness and longevity[1].
Scientifically, ashwagandha is known as an adaptogen, which primarily helps the body to manage stress, reduce anxiety and depression and improve concentration and memory. Ashwagandha root extract has a wide range of clinically proven health benefits, including lowering cortisol, (known as the stress hormone) [4, 5, 6]. Some men taking Ashwagandha supplements see an increase in their testosterone levels, fertility and enhance sexual function[7, 8], whereas women found their perimenopause symptoms were alleviated[9]. Ashwagandha has been used successfully to support weight control[10]. Studies with athletes looking to increase strength, cardiorespiratory endurance, and to recover fast from activity, show they can benefit from taking supplements containing ashwagandha [11,12]. Improving muscle strength and endurance has also been researched in the elderly showing that ashwagandha helps to maintain their quality of life. Ashwagandha can improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels. Its anti-inflammatory properties have been used to reduce chronic inflammation. Studies show that ashwagandha improves mitochondria and increases telomerase activity[13,14]. These studies on telomerase and along with work showing Withania somnifera root extract extends lifespan of C. elegans, scientifically support its use in healthy-aging and its traditional role in Rasayana[15]. Ashwagandha root has other properties that are very relevant to today’s beauty consumer. Peer reviewed research confirms the beauty benefits of using ashwagandha root extract topically such as skin moisturising and firming[16]. Ashwagandha strengthens hair making it less prone to breakage. It stimulates hair follicles and inhibits the loss of melanin so maybe ashwagandha can be useful for slowing premature hair greying[17]. In India, ashwagandha has long been considered as a general tonic for overall health and to help provide relief from a variety of health conditions.
The scientific basis of how ashwagandha helps the body cope with these conditions is beginning to be understood. Search engines such as Google Scholar and Research Gate, report over 27,000 publications on ashwagandha, with nearly 70 review articles published in the first two months of 2024. Ashwagandha has been mainly studied as a health supplement, however, the number of publications focussing on its topical effects is increasing. When studying or formulating with a botanical, a readily available, full spectrum powdered extract (so retaining the traditional efficacy), free from diluents and preservatives and easy to dissolve, is the gold standard. Scientists prefer to use the same source of material as other research groups so their results and conclusions can be reliably compared. For these reasons KSM-66 Ashwagandha root extract has featured in numerous research papers, and it well deserves the accolade of being the most studied ashwagandha root extract [18].
Bioactive Chemical Constituents
Although research on stress management has centred around three of ashwagandha’s main withanolides (the C28-steroidal lactones, withaferin A, withanolide D and withanolide A), there is a whole array of diverse multifunctional bioactive compounds present in ashwagandha, including alkaloids, other steroidal lactones, sitoindosides, flavonoids and saponins[19]. Each of these classes of molecules contains many individual types, for example, there are at least 40 different withanolides and 12 identified alkaloids in ashwagandha root including withanine, ashwagandine and ashwagandinine. Many of the Withania somnifera root constituents are known to have skin benefits. Some researchers see withaferin A as potential active for treating skin diseases such as dermal fibrosis and hyperpigmentation[20]. To take just one example, Withania somnifera root contains the flavonoid, quercetin, which is multifunctional with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, MMP inhibiting properties, can improve skin barrier function and offer some protection from UV. Many of the other constituents of ashwagandha root are also multifunctional. The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases [21], lists 127 activities associated with Withania somnifera root. These activities include anti-inflammatory action, which can be due to any and all of the following constituents: beta-sitosterol, chlorogenic acid, linoleic acid, n-hentriacontane, quercetin, rutin, scopoletin, stigmasterol, withaferin-A and withanolide-D. The database reports that much of the antioxidant properties of Withania somnifera root will come from caffeoylquinic acid, beta-sitosterol, campesterol, chlorogenic acid, cysteine, quercetin, rutin, scopoletin and stigmasterol. Beta-sitosterol, chlorogenic acid, quercetin, rutin, scopoletin and withaferin A will contribute to Withania somnifera root reported antimicrobial properties. The complex composition of ashwagandha root extract highlights why it is so important to use a full spectrum ashwagandha root extract when studying ashwagandha’s efficacy or formulating ashwagandha products.
Safety and Cosmetic Applications
With thousands of years of safe use behind it and with GRAS status, ashwagandha root is generally considered safe when used as instructed, in health supplements and cosmetics[22]. The health supplement regulations ensure products pass stringent safety checks and consumers are always advised to "consult your doctor/healthcare provider before use." International regulations demand that cosmetic materials are tested for safety before they can be offered for sale. As well as passing the other industry recognised safety tests, the in vitro skin sensitization study of KSM-66 Ashwagandha Root extract showed that it is a non-sensitizer and is safe for use. The MTT assay showed the root extract powder was non-toxic at the concentration of 1, 10 and 50 mg/ml, compared to the untreated control and that it is non-irritant to eyes using HET-CAM method. A recent randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled study on a lotion with 8% ashwagandha full spectrum root extract, confirmed that it is safe to apply to facial skin[16]. The study looked at both the safety and efficacy of ashwagandha root extract. Participants were all healthy individuals with photodamaged skin. Fifty-six men and women aged between 18 and 60 years, with Fitzpatrick phototype III-VI skin grade, applied to their faces immediately after cleansing, either a lotion with ashwagandha root extract, or a control placebo. The lotions were applied in the morning and then again at a minimum of 8 hours later for 60 days. Each application of 1ml was massaged into their skin until it was well absorbed.
Safety was assessed on all 56 participants. Local reactions and the number and proportion of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were recorded over the 60-day treatment.
Because 3 subjects left the study before they could be assessed for changes in their skin properties, only 53 subjects, (27 in the group using the lotion with ashwagandha root extract), underwent Physician Global Assessment (PGA) receiving response scores for the following: skin wrinkles, pores, hydration/moisture, skin brightness/tone, and pigmentation. Changes in transepidermal water loss (TEWL), melanin index, hydration and skin elasticity (R2 ratio), were also determined on these 53 individuals. Replicate measurements were taken, and analysis of variance (ANOVA) used to assess the effect of the treatment as per the protocol. Two groups were compared for differences using a t-test for continuous data or a Mann-Whitney U test for ordinal data. Adverse events were compared between two groups using the chi-square test.
Results - Safety
The adverse events reported during the study were similar for the group using the lotion with ashwagandha root extract and for those using the control lotion (p=0.718; chi-square test). During the study, 4 participants using the lotion with ashwagandha root extract and 5 participants from the placebo group, reported adverse events (local irritation, erythema, and swelling). 2 subjects from both groups reported local swelling. 2 subjects from the group using the lotion with ashwagandha root extract and one member of the placebo group reported erythema. Local irritation was reported by two participants in the placebo group. All the reported events were of mild severity and resolved quickly without intervention and the subjects involved continued until the end of the study. The authors were satisfied that up to 8% ashwagandha full spectrum root extract as safe to use topically.
Results - Skin benefits
Physician Global Assessment (PGA) of the skin characteristics for all participants before the lotions were applied were very similar. When these characteristics were reassessed at day 60 of the clinical trial, the lotion with ashwagandha root extract clearly outperformed the placebo lotion. Figure 3 shows the results for the ashwagandha full spectrum root extract lotion next to the results for the placebo cream. Statistical analysis of the data showed significant differences between the two treatment groups. Although the mean PGA scores were not dramatically different between groups, the p-value from the total analysis was <0.0001, indicating that the improvements detected are due to the lotion with ashwagandha full spectrum root extract.
Summary and Future Outlook
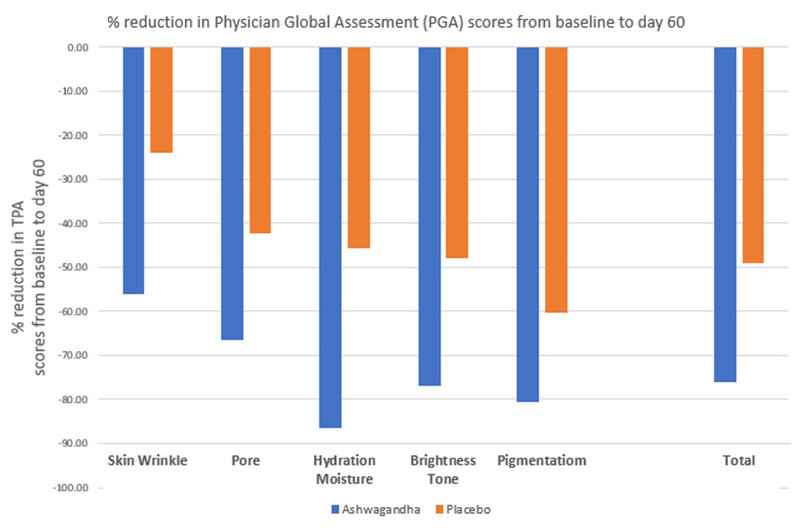
Figure 3. % Change in Physician Global Assessment (PGA) scores from baseline to day 60
Graph prepared using data published data from Narra et al., 2023 [15].
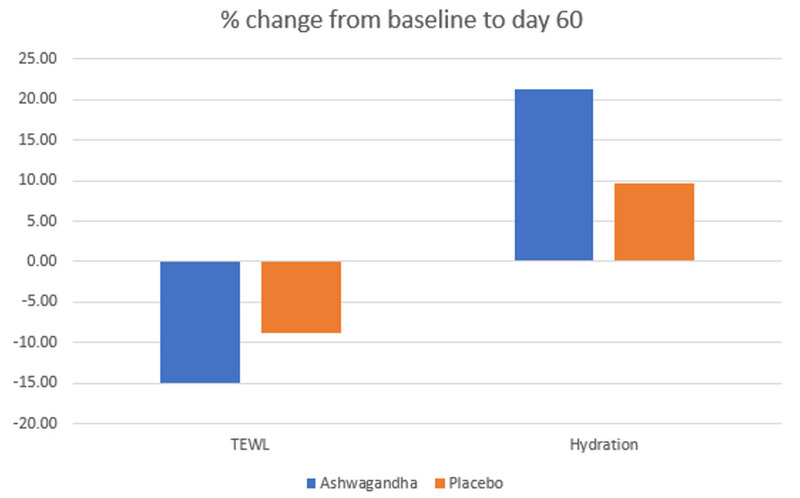
The subjects using the lotion containing ashwagandha root extract also saw a significant reduction in transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and an increase in skin hydration and elasticity (figure 4).
Figure 4. % Change in TEWL and hydration from baseline to day 60.
Graph prepared using data published data from Narra et al., 2023[15].
A Cutometer® Dual MPA 580 was used to assess skin elasticity of 53 trial participants. The R2 ratio, (the value when the Cutometer is at complete relaxation and immediately after the suction. The larger the ratio, the more elastic the skin). At the end of the 60 day trial skin elasticity had increased by 16.34% for the subjects using the lotion with the ashwagandha root extract compared with an increase of 3.73% for those using the placebo cream.
Well-being
Participants in the study reported scores for quality of life using a validated questionnaire. This self-reporting evaluates the physical and mental state of the responders. The results indicated that the subjects in the clinical trial who used the lotion with ashwagandha improved both physically and mentally, when compared with those using the placebo. The authors concluded that topical application of lotion containing ashwagandha root extract was safe, improved the skin condition of photoaged healthy individuals and also their well-being.
HAIR
Ashwagandha is used in hair products as well as in skin care, however out of over 200 cosmetics listed on incidecoder.com, which have Withania Somnifera Root Extract in their INCI lists, less than 10 were hair products. Research into the efficacy of Withania Somnifera Root Extract on hair is equally scarce. One, double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, two arm, parallel, comparative study found that a topical ashwagandha serum improved hair growth and hair health indicators. They tested the serum with 5% ashwagandha root extract on 61 Healthy adults between 18 and 45 years with mild to moderate hair loss. The participants were assessed at Day 1 and Day 75 for changes in 60 Seconds Hair Comb, Trichoscan analysis, Hair Pull test, Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) and QoL using Hair-specific Skindex-29 where scores reflect emotions, symptoms, and functioning on a scale of 0 (no effect) to 100 (maximum effect)[16]. In the study ashwagandha topical serum boosted hair growth and health markers. In the 60 second hair comb experiment ashwagandha serum lowered hair loss by 45% for hair with bulbs and 69% for hair without bulbs. Trichoscan analysis in the subjects using ashwagandha serum showed (compared to the placebo) that hair density had increased by 4.6%, hair growth improved by 7.3%, hair thickness increased by 3.6%, and the increase in the percentage of hair in the growing anagen phase increased by 5%. Additionally, the percentage of hair in the shedding telogen phase was reduced by 8% and the hair pull test found a 69% reduction in the number of hairs pulled out. From the Skindex-29 survey it could be seen that hair-related symptom scores for the group using ashwagandha serum, decreased by 17%, while hair-related functioning scores increased by 21%. The emotional impact scores for this group were reduced by 12%, and the total hair-specific life quality impact was lower by 18%. In this study the topical use of an ashwagandha root serum displayed considerable quantitative improvements in hair qualities linked to hair growth, loss, density, and the quality of life impact in healthy adults [16].
Summary and Future Outlook
Ashwagandha has been used for thousands of years in India's traditional Ayurvedic medicine to support the mind-body and to help maintain youth, strength and vitality. Research is driving Worldwide interest in this prince of herbs. Extracts of this woody shrub’s roots have the INCI name Withania Somnifera Root Extract and are recognised by regulators as safe when used at the recommended levels. Its benefits as a supplement are anti-stress, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-aging, energy boosting, neuroprotective effects, boosting muscle growth via increased testosterone and protein synthesis, improving cardiorespiratory endurance as well as improving perimenopause, sexual and reproductive parameters. From the beauty industry’s point of view, cosmetics products with ashwagandha root extract can reduce wrinkles and fine lines, improve pores, moisturisation, skin brightness and tone as well as even pigmentation. The scientific basis of these attributes is beginning to be explained. Ashwagandha root contains a very large number of bioactive molecules, which is why it is important to use a full spectrum extract when studying or formulating with ashwagandha. Although studies are limited, ashwagandha root extract also has been shown to have hair benefits such as reducing hair loss, improving thickness, density and growth. With today’s consumers demanding natural holistic solutions, ashwagandha the ancient ayurvedic natural adaptogen, is finding its rightful place in modern beauty.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.

Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- Ghuraiya, S., Gurjar, M., Garg, A.K., and Ojha, K. Rasayana as a Unique Therapy of Ayurveda: A Conceptual Review. (2019). World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research Volume 8, Issue 13, p527-535 https://wjpr.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/article_issue/1575105103.pdf
- Malík, M., Tlustoš, P. Nootropic Herbs, Shrubs, and Trees as Potential Cognitive Enhancers. Plants (Basel). (2023) Mar 18;12(6):1364. doi: 10.3390/plants12061364. PMID: 36987052; PMCID: PMC10056569.
- EU inventory of cosmetic ingredients - CosIng. https://ec.europa.eu/growth/tools-databases/cosing/
- Gopukumar K, Thanawala S, Somepalli V, Rao TSS, Thamatam VB, Chauhan S. Efficacy and Safety of Ashwagandha Root Extract on Cognitive Functions in Healthy, Stressed Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) Nov 30;2021:8254344. doi: 10.1155/2021/8254344. PMID: 34858513; PMCID: PMC8632422
4. Chandrasekhar, K., Kapoor, J., and Anishetty, S. A Prospective, Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a High-Concentration, Full-Spectrum Extract of Ashwagandha Root in Reducing Stress and Anxiety in Adults. (2012). Indian J Psychol Med. 34(3) p255-262 PMID: 23439798 PMCID: PMC3573577 DOI: 10.4103/0253-7176.106022 - Adrian L. Lopresti, Stephen J. Smith,. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) for the treatment and enhancement of mental and physical conditions: A systematic review of human trials, Journal of Herbal Medicine. (2021). Vol. 100434, ISSN 2210-8033,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hermed.2021.100434.(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2210803321000142)
- Porta, M.D, Maier, J and Cazzola, R. Effects of Withania somnifera on Cortisol Levels in Stressed Human Subjects: A Systematic Review. (2023) Nutrients 15, no. 24: 5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245015
- Ambiye, V. R., Langade, D., Dongre, S., Aptikar, P., Kulkarni, M., Dongre, A. Clinical Evaluation of the Spermatogenic Activity of the Root Extract of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) in Oligospermic Males: A Pilot Study. (2013).Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:571420. doi: 10.1155/2013/571420. Epub Nov 28. PMID: 24371462; PMCID: PMC3863556. Clincal Evaluation of the Spermatogenic Activity
- Gopal, S., Ajgaonkar, A., Kanchi, P., Kaundinya, A., Thakare, V., Chauhan, S. and Langade, D. Effect of an ashwagandha (Withania Somnifera) root extract on climacteric symptoms in women during perimenopause: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. (2021). J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Research, 47(12), 4414–4425.
- Choudhary, D., Bhattacharyya, S., and Joshi, K. Body Weight Management in Adults Under Chronic Stress Through Treatment With Ashwagandha Root Extract: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. (2017). Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine. 22(1):96-106. doi:10.1177/2156587216641830
- Bonilla, D.A., Moreno, Y., Gho, C., Petro, J.L., Odriozola-Martínez, A., Kreider, R.B. Effects of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) on Physical Performance: Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. (2121) J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. Feb 11;6(1):20. doi: 10.3390/jfmk6010020. PMID: 33670194; PMCID: PMC8006238.
- Choudhary, B., Shetty, A., and Langade, D. G., Efficacy of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera [L.] Dunal) in improving cardiorespiratory endurance in healthy athletic adults. (2015) Ayu. Jan-Mar;36(1):63-8. doi: 10.4103/0974-8520.169002. PMID: 26730141; PMCID: PMC4687242.
- Ragurman, V.R., Subramaniam, J.R. Withania somnifera Root Extract Enhances Telomerase Activity in the Human HeLa Cell Line. (2016) Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 7, 199-204. doi: 10.4236/abb.2016.74018.
- Sharma R, Martins N. Telomeres, DNA Damage and Ageing: Potential Leads from Ayurvedic Rasayana (Anti-Ageing) Drugs. (2020). J Clin Med. Aug 6;9(8):2544. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082544. PMID: 32781627; PMCID: PMC7465058.
- Kumar, R., Gupta, K., Saharia, K., Pradhan, D., Subramaniam, J.R. Withania somnifera root extract extends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Ann Neurosci. 2013 Jan;20(1):13-6. doi: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.200106. PMID: 25206003; PMCID: PMC4117092.
- Narra, K., Naik, S. K., Ghatge, A. S. A Study of Efficacy and Safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) Lotion on Facial Skin in Photoaged Healthy Adults. (2023). Cureus 15(3): e36168. DOI 10.7759/cureus.36168
- Yerram, C., Jillella, A., Reddy, V. Effects of Withania somnifera root extract serum application on hair health in healthy adults: A prospective, double-blind, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled study. (2023). Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, Volume 14, Issue 6, 2023, ISSN 0975-9476, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaim.2023.100817.
- KSM-66 Webpage: https://ksm66ashwagandhaa.com/ksm-66/what-is-ksm-66/
- Mirjalili, M.H., Moyano, E., Bonfill, M., Cusido, R.M., Palazón, J. Steroidal lactones from Withania somnifera, an ancient plant for novel medicine. Molecules. (2009) Jul 3;14(7):2373-93. doi: 10.3390/molecules14072373. PMID: 19633611; PMCID: PMC6255378.
- Simona, B., Vesa, C.M., Abid, A., Behl, T.,Tit, D.M., Purza, A.L., Pasca,B., Todan, L.M., and Endres, L. Withaferin A—A Promising Phytochemical Compound with Multiple Results in Dermatological Diseases. (2121) Molecules 26, no. 9: 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092407
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. 1992-2016. Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases. Home Page, http://phytochem.nal.usda.gov/ http://dx.doi.org/10.15482/USDA.ADC/1239279
- Choudhary, D., Bhattacharyya, S., and Bose, S. Efficacy and Safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal) Root Extract in Improving Memory and Cognitive Functions. (2017). J Diet Suppl. Nov 2;14(6):599-612. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2017.1284970. Epub 2017 Feb 21. PMID: 28471731.
- Vaidya, V.G., Gothwad, A., Ganu, G., Girme, A., Modi, S.J., and Hingorani L. Clinical safety and tolerability evaluation of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal (Ashwagandha) root extract in healthy human volunteers. (2023) J Ayurveda Integr Med. Dec 27;15(1):100859. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2023.100859. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38154316; PMCID: PMC10784694.
