Inclusivity
on
Skin care

peer-reviewed
An alfalfa quintessence to the benefit of a plural beauty
MÉLANIE COIRIER, MÉLANIE HUMEAU, HÉLÈNE MUCHICO*, ÉLODIE AYMARD, BRIGITTE CLOSS
*Corresponding author
SILAB, Brive, France
ABSTRACT: In the cosmetics industry, “plural beauty” is a concept that has been rising with the diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) movement. In line with this idea of considering all skin specificities, SILAB identified the main cutaneous characteristics of consumers in terms of ethnicity, age, and gender. This approach highlighted that the three major beauty axes responding to universal expectations are all regulated by biological mechanisms taking effect in both the dermis and epidermis. The aim of the study was therefore to demonstrate how a Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract can respond to the needs of all skin types through a transversal action on both the dermis and the epidermis.
??????????????????
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”

Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
Introduction
Towards more inclusivity
Throughout history, society continuously evolved its ideal beauty norms. Despite inherent cultural differences, the cosmetic industry long promoted the west’s products. The rise of the diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) movement however has prompted the cosmetics industry to develop ultra-personalized care by considering all skin types as well as gender and age. Indeed, whether masculine, feminine, young, old or from the four corners of the world, all skins have their particularities.
Identifying the main skin specificities
Skin colour, depending on the presence of melanin, represents the major difference between ethnic groups (1). Indeed, lighter skins are characterized by low melanin levels, making them more vulnerable to photoaging, and the premature emergence of pigmentation spots. They are also more fragile, and generally reflect a premature loss of elastin and collagen fibre structure, leading to the early appearance of very pronounced wrinkles. Melanin rich skins better resist the negative side effects of photoaging. Their dermis is also more compact and the collagen network denser than those of fairer skins, thus delaying the onset of wrinkles. That said, a heterogenous pigmentation can lead to irregular skin tone. In fact, their skin's very high transepidermal water loss explains why they are more prone to skin dryness (figure 1).
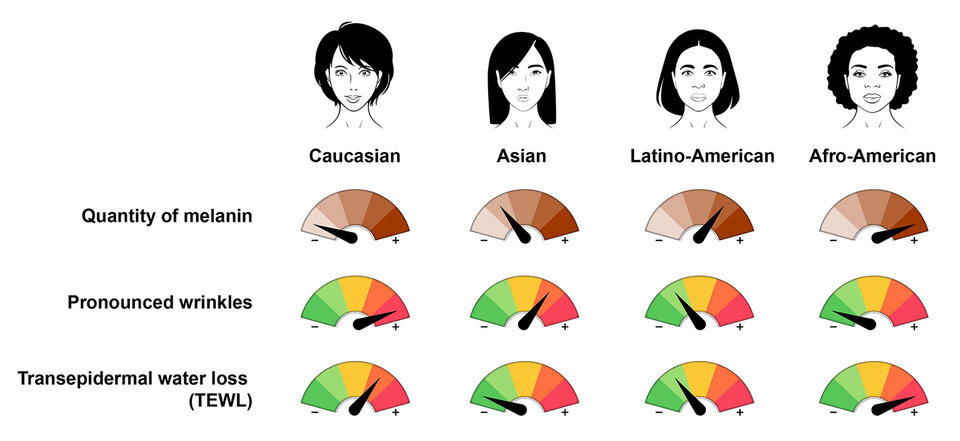
Figure 1. Variation of certain cutaneous parameters according to different ethnic groups.
Physiological needs also differ based on age. Young consumers generally seek solutions focused on the quality of their skin, compared to mature skins that wish to erase ageing signs.
Regarding gender, despite significant biological differences, men and women share similar skin care moisturizing and anti-ageing expectations.
Defining universal expectations
Thanks to this approach, three major beauty axes that respond to universal expectations of skin care consumers were identified. The first criterion is a beautiful skin quality, influenced by skin hydration and fine skin texture for a smoothed microrelief. An even, radiant complexion free from the blemishes associated with post-inflammatory scarring and skin ageing represents the second pillar. The last aspect refers to reduced signs of ageing thanks to firmer skin and faded wrinkles.
These three axes are run by biological mechanisms taking effect in the dermis and epidermis.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Stimulating epidermal functions
Exploratory and predictive study on reconstructed epidermis (SILABSKIN® RE)
Human keratinocytes were cultivated at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2. After 14 days, the culture medium was discarded and replaced with medium containing the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract at 0.5% (V/V). Reconstructed epidermis were recovered and total RNA was extracted 24 hours later. Total RNAs were labelled and hybridized on SurePrint G3 Human GE V3 8x60K microarrays (Agilent Technologies). The data were then analysed using R software. Significantly modulated transcripts were analysed using DAVID (Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery). Using databases (Kegg, Reactome, etc.), transcriptome pathways modulated by the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract have been identified.
Validation of the gene expression on reconstructed epidermis
Human keratinocytes were cultivated according to thesame process as for the exploratory and predictive study. RNAs were reverse transcripted and the complementary DNAs obtained were analysed with the quantitative PCR technique. Fluorescence incorporation (SYBR Green) was quantified continuously with an LC480 LightCycler thermocycler (Roche). Analysis of Ct (relative quantification) was done with LC480 software (Roche).
Study of protein synthesis on reconstructed skin (SILABSKIN® FT)
Skin models were obtained by assembling sheets of young (< 30 years) and old (> 60 years) fibroblasts and keratinocytes. The resulting reconstructed skin were then incubated at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2 for 6 days. During this period, they were treated every two days with the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract at 0.5% (V/V). Then, they were fixed, dehydrated and embedded in paraffin before preparing sections with a microtome (Leica). The synthesis of Ki-67, loricrin, claudin-1, integrin β4, collagen VII, aquaporin 3 or laminin 332 were then analysed by using immunohistofluorescence. Visualization was done with an IX 70 microscope (Olympus) coupled to an image acquisition system (NIS-Elements software, Nikon). Neutral lipids were stained by incubating 3D skin model sections with BODIPYTM 493/503. Microscopic observations were made with an LSM700 confocal microscope (Zeiss) coupled to a Zen Blue image analysis system (Zeiss). Quantitative analysis of the images was conducted using an image analysis script developed in-house with Python language. The results are expressed in arbitrary units (AU).
Reinforcing dermal matrix quality
Cell culture
Human fibroblasts obtained from young (30 - 40 years) or mature (> 60 years) men or women of different ethnicities (Caucasian, Asian, Afro-American) were seeded and incubated at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2.
Study of collagen I synthesis
After 4 days of culture, fibroblasts were treated with the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract at 1.00% (V/V). Cells were then incubated for 72 hours. Supernatants were recovered and collagen I synthesis investigated by ELISA assay.
Study of MMP-1 synthesis
After 3 days of culture, fibroblasts were treated with the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract at 0.5% or 1.0% (V/V). Irradiations were conducted with a UV lamp (BioSun, Vilber Lourmat) emitting a UVA intensity of 10 J/cm2. The culture medium was discarded and replaced with medium containing the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract at 0.5% or 1.0% (V/V) for 48 hours. Supernatants were recovered and MMP-1 synthesis evaluated by ELISA assay.
Studies on volunteers
Description of the panels
The performance of the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract was evaluated thanks to five clinical studies on mixed gender groups with young and mature volunteers from four different ethnicities (Caucasian, Latin-American, Afro-American and Asian).
Hydra-smoothing effect
The hydrating effect of the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract at 2.5% was determined by Corneometer® after 21 days of twice daily application by the young Caucasian panel (half of face) and by the young Latin-American and Afro-American panels (entire face).
In the same application conditions, the smoothing effect was determined by analysing the microrelief as well as the skin grain of volunteers from the following panels: Caucasian (by fringe projection and clinical scoring, respectively), Latin-American (by Visioscan® VC98 and image analysis) and Afro-American (by clinical scoring).
Complexion-perfecting effect
The effect of the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract on complexion radiance was assessed in young Caucasian, Latin-American, Afro-American panels as well as in mature Caucasian and Asian panels. The young panels followed the same application conditions. For mature panels, the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract was applied at 2.5% for 42 days, to the entire face for the Caucasian panel and to half of the face for the Asian panel. The methods used were the clinical scoring for the young and mature Caucasian panel as well as for the young Afro-American panel and the Skin-Glossymeter® for the young Latin-American and mature Asian panels.
The effect on post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation spots was assessed on Latin-American volunteers (using Visioface® and image analysis) and on the Afro-American panel (using clinical scoring). The effect on senescence spots was determined on mature Caucasian (using C-Cube) and Asian volunteers (using Mexameter®).
Anti-ageing effect
The anti-ageing benefits of the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract have been demonstrated in mature Caucasian and Asian volunteers by determining the anti-wrinkle (by fringe projection) and firmness (by Cutometer®) effects.
Statistical analysis
Results obtained were compared with Student’s t test with a significance threshold set at 5%.
RESULTS
Stimulating epidermal functions
Hydration, quality of cutaneous microrelief, and complexion’s uniformity and radiance depend on many biological mechanisms taking place in the epidermis. In fact, it plays many roles including those in the physical and water barrier, the immune barrier, and the anchoring of the epidermis to the dermis (2).
Exploratory and predictive study
To explore and predict the biological pathways modulated by the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract in reconstructed epidermis, about 26,000 genes were analysed using transcriptomic chips. 15,000 of them were expressed by SILABSKIN® RE reconstructed epidermis.
The bioinformatic analysis of these genes revealed an enrichment of 4 signalling pathways modulated by the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract: the mature cornified envelope, the lipid metabolism, the mature immune system and the interactions with laminin - receptor/Extracellular matrix (ECM) interaction.
Following this initial analysis, the pathways identified above were linked to epidermal functions: the mature cornified envelope and the lipid metabolism were linked to the physical and water barrier, the mature immune system was linked to the immune barrier and the interactions with laminin - receptor/ECM interaction were linked to the anchoring of the epidermis to the dermis.
Validation of the gene expression
To validate the effect of the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract on the biological pathways initially identified using the transcriptomic chips (physical and water barrier, immune barrier, epidermis-dermis anchoring), 56 genes of interest representative of the different pathways were analysed: 33 genes for the physical and water barrier; 12 genes for the immune barrier, including 4 pro-inflammatory genes; 11 genes for anchoring the epidermis to the dermis.
Among these 56 genes studied, the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract significantly boosts the expression of 31 genes regulating the physical and water barrier, 6 genes regulating the immune barrier, and 11 genes regulating anchoring the epidermis to the dermis. It is important to note that the analysis of 4 genes regulating the immune barrier, which are linked to inflammation, shows that the natural active ingredient has no pro-inflammatory action. These results demonstrate that the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract plays a transversal role on the epidermal barrier by positively modulating 92% of the genes involved in these three epidermal functions.
Study of protein synthesis
Proteins representative of the physical and water barrier (Ki-67, loricrin, claudin-1, intercorneocyte lipids and aquaporin 3) and epidermis to the dermis anchoring (integrin β4, laminin 332, collagen VII) were measured to validate the capacity of the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract to improve epidermal functions. The results show that, in young reconstructed skin the natural active ingredient significantly boosts the synthesis of molecules involved in the physical and water barrier (proteins and neutral lipids), as well as proteins involved in anchoring the epidermis to the dermis. In old reconstructed skin, it also significantly restores the synthesis of all protein markers and neutral lipids (figure 2). The Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract therefore improves and maintains a functional epidermal barrier.
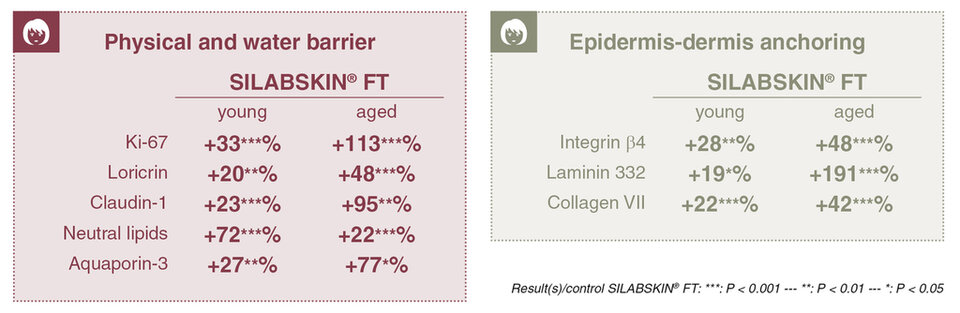
Figure 2. Study of proteins involved in the physical and water barrier and in epidermis to the dermis anchoring.
Reinforcing dermal matrix quality
The dermis, through the syntheses of collagen I and of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), plays a central role in avoiding visible signs of ageing, such as the appearance of wrinkles and loss of firmness on the face.
Tested on fibroblasts of different genders, ages, and ethnicities, the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract enhances matrix quality by significantly boosting the synthesis of collagen I and significantly reducing the synthesis of MMP-1 (figure 3).
The Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract therefore preserves and reinforces the dermal matrix.
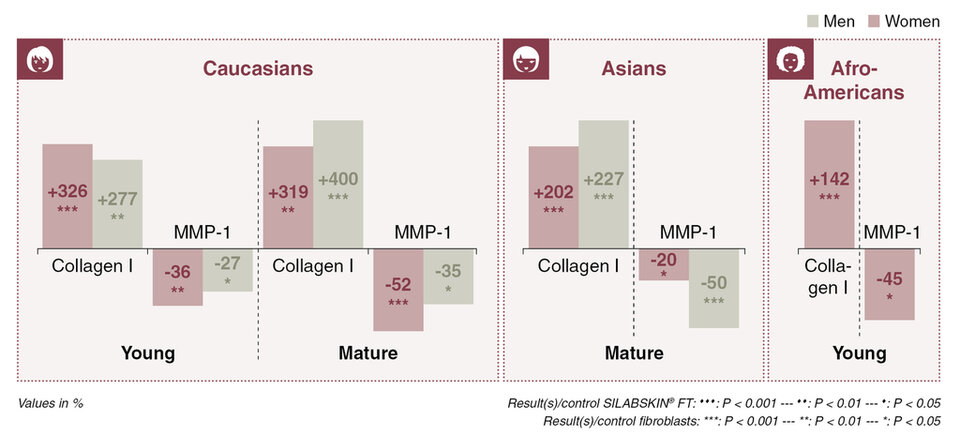
Figure 3. Study of collagen I and MMP-1 synthesis by fibroblasts treated with the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract.
Studies on volunteers
Tested on panels of different genders, ages, and ethnicities (Afro-Americans, Latin-Americans, Caucasians, and Asians), the natural active ingredient demonstrates multiple cosmetics benefits.
Hydra-smoothing effect
After treatment, skin hydration is significantly increased in young Caucasian (+14.6%, P < 0.05), Latin-American (+43.3%, P < 0.001) and Afro-American (+13.0%, P < 0.05) volunteers as of 7 days. In the same conditions, the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract also significantly smooths the microrelief in Afro-American (-9.5%, P < 0.05), and Caucasian (-6.1%, P < 0.01) subjects (effect not seen in the Latin-American panel). After 21 days, the hydrating effect continues, and the smoothing effect intensifies and becomes significantly visible in Latin-American volunteers (-13.2%, P < 0.01). In addition, as of 7 days as well, the visibility of pores is reduced in young Caucasian (-12.7%, P < 0.01), Afro-American (-15,7%, P < 0.001), and Latin-American volunteers (-10.6%). These data confirm the hydra-smoothing effect of this natural active ingredient.
Complexion-perfecting effect
The Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract increases reflection of the skin as of 15 minutes (young Caucasian: +7.4%, P < 0.001; young Afro-American: +6.6%; mature Caucasian: +12.2%, P < 0.01; mature Asian: +3.2%, P < 0.05). This effect continues after 7 and 21 days for the young panels and after 42 days for the mature panels.
Also, it significantly reduces the visibility of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation spots in young Latin-American (-17.5%, P < 0.05) and Afro-American (-8.9%, P < 0.001) subjects as of 7 days, and limits senescence spots in mature Caucasian (-5.7%, P < 0.05) and Asian (-18.2%, P < 0.001) volunteers as of 21 days.
The Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract therefore enhances complexion radiance immediately and continuously and evens the complexion.
Anti-ageing effect
In just 7 days, wrinkles are reduced by 7.9% (P < 0.01) in Caucasian volunteers and by 11.7% (P < 0.01) in Asian volunteers. The skin also regains its firmness after 42 days of application (Caucasian: +15.7%, P < 0.001; Asian: +10.8%, P < 0.001).
All these data demonstrate that the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract responds in just 7 days to a wide range of issues, targeting the three major issues of skin beauty (figure 4).
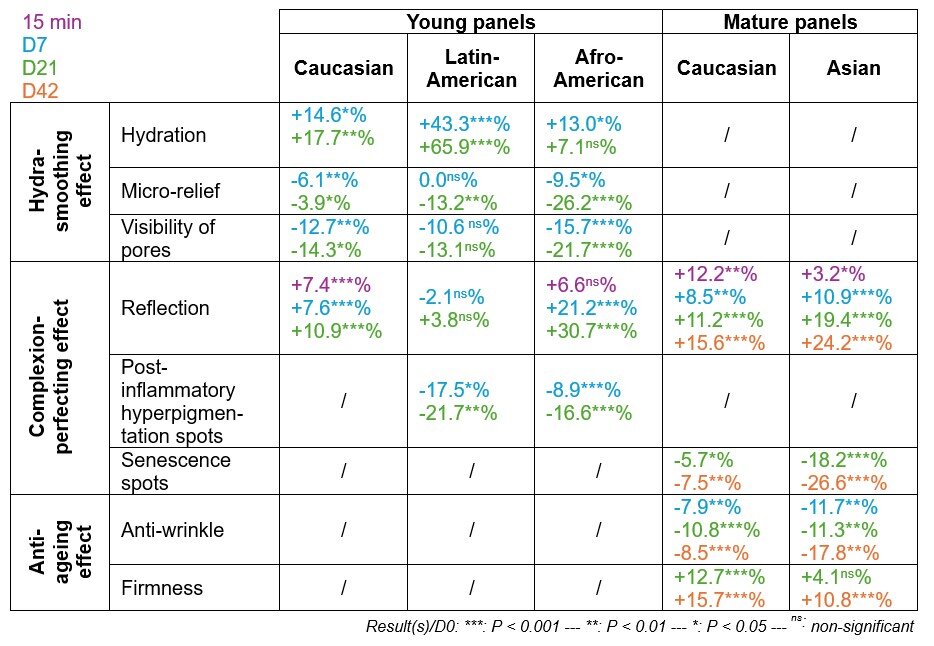
Figure 4. Summary table of the in vivo effects of the Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract.
Conclusion
SILAB has banked on a cross-disciplinary approach by mastering the remarkable properties of alfalfa, which has already demonstrated its beneficial action on the epidermis and dermis (3).
The resulting Water & Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) Extract is therefore a multi-functional natural active ingredient offering a large scale of cosmetic benefits to sublimate all skins, including ethnicity, age, and gender.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
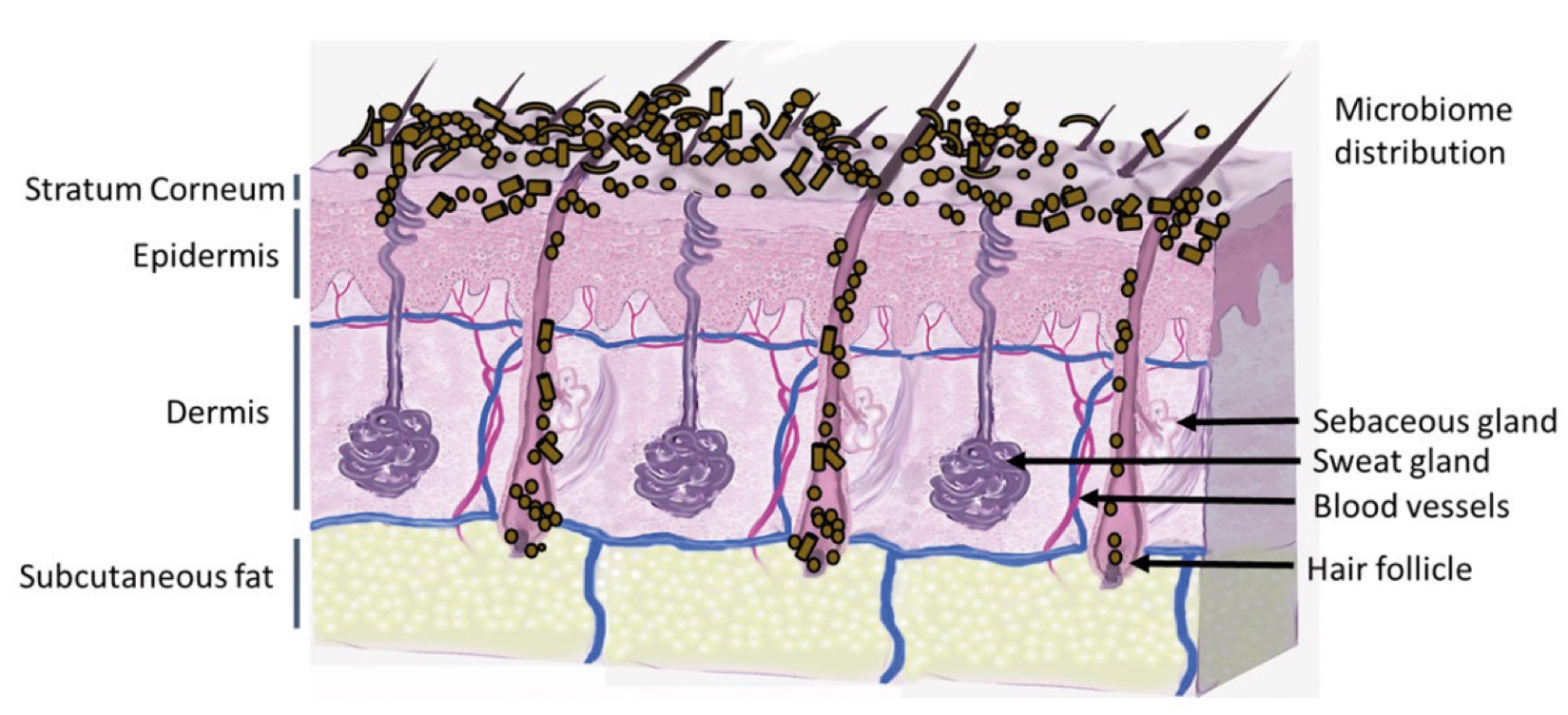
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- Rawlings, A.V. Ethnic skin types: are there differences in skin structure and function?. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2006 28: 79-93. DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-2494.2006.00302.x
- Lee HJ, Kim M. Skin Barrier Function and the Microbiome. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):13071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113071
- Jouandeaud M., Bordes S., Soulie C., Closs B., The influence of oligosaccharides on skin aging: an alternative to retinoids, Cosmetics & Toiletries, 2004 119(6): 67-76 https://img.cosmeticsandtoiletries.com/files/base/allured/all/document/2023/04/CT_119_06_067_07.6436d496af965.pdf
