Natural Ingredients
on
Skin care
peer-reviewed
Natural cosmetics: Trends and requirements for a sustainable future
VIKTORIA POTKO
Certification and Global Market Development Manager, NATRUE, Brussels, Belgium
ABSTRACT: The natural cosmetics industry has experienced significant growth in recent years as consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability, wellbeing, and environmental consciousness. This shift in consumer preferences has led to the evolution of the Natural and Organic Cosmetics (NOC) market, placing greater emphasis on transparency, ethical sourcing, and sustainable practices that benefit both people and the planet. In this article, we explore the evolving landscape of the natural cosmetics sector, focusing on key trends, changing consumer requirements, and anticipated regulatory developments in 2024.
The natural and organic cosmetics (NOC) market has seen substantial growth and transformation, driven by consumer demand for more sustainable alternatives to conventional beauty products. Consumers are increasingly demanding and concerned about their actions and the footprint they will leave on the planet, and this translates into all their choices. What was once dominated by conventional synthetic ingredients has now transitioned towards sustainability and natural formulations; hence consumers look for products with lower environmental impact, based upon renewables and which are free of petrochemical-based synthetic substances and silicones. Product innovation in the quality of the raw materials and production processes has become the lifeblood of this industry. Manufacturers are now aligning themselves with the ethics of the times, creating products that not only enhance beauty but also respect the planet.
Additionally, the rise of social media and digital platforms has facilitated greater awareness and access to information, allowing consumers to make informed decisions about the products they use. This has prompted cosmetics companies to reformulate their products, incorporating natural substances and adopting cleaner, verifiable, and transparent production processes, such as certification. As a result, the NOC market has witnessed increased competition, innovation, and diversification, with brands seeking to capture the attention of environmentally conscious consumers.
THE NEW CONSUMER: Cautious and conscious
We are seeing extensive consumer studies trying to understand preferences and priorities in the NOC market. These studies reveal that consumers place a premium on product efficacy, safety, and authenticity. In fact, 85% of consumers would be willing to pay more for beauty products with proven efficacy or benefits (1). Key factors influencing purchasing decisions include the presence of natural and organic ingredients, ethical sourcing practices, product innovation, and clear labelling. Interesting is the fact that over 30% of consumers buy from brands that support social and political issues aligned with their values, while around 25% of them boycott brands or companies that don’t share their political or social beliefs (2).
Consumers also express a growing interest in sustainability, with many seeking products packaged in recyclable or biodegradable materials. Nevertheless, their increased awareness is also reflected in their growing demand for products and labels that can be proven, as transparency emerges as a crucial factor for them, with trust playing a pivotal role in purchasing decisions. This was evidenced by a European Commission’s study (3), which found that 53.3% of the claims examined were vague, misleading, or unfounded, and 40% were unsubstantiated, highlighting the need for greater transparency and accountability in the industry.

TRENDS IN THE NATURAL COSMETICS SECTOR
Sustainability stands out as the predominant trend. It continues to be a key focus area within the natural cosmetics sector, encompassing initiatives to conserve resources, increase efficiency, and reduce waste. From waterless products to upcycled ingredients or multifunctional cosmetics, companies are exploring innovative ways to minimize environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
The integration of sustainable practices into formulation processes involves sourcing raw materials responsibly, minimizing waste, and reducing carbon footprint throughout the production chain. These approaches translate into everything from more waterless products to greener methods for raw material extraction and production, to eco-designed products, to reducing waste via upcycling, to greater use of ingredients with positive social and reduced environmental impact (increased use of biodegradable substances). Brands are exploring innovative ingredients and manufacturing techniques to create high-performance products that are both effective and that do not harm the planet. In this sense one of the priority actions in the sector is to source responsibly, including by screening supply chain risks: “In the beauty sector, there are already strong incentives to engage with biodiversity, given its central role as iconic ingredients and inspiring stories behind products and brands. In fact, companies should be considering how to scale up these biodiversity-friendly practices beyond iconic ingredients to a wider range of ingredients used in beauty products.” – highlighted UEBT (4).
Same thing happens when we try to integrate sustainable practices into packaging, as brands are increasingly adopting eco-friendly packaging solutions such as mono recycled materials, bio-based plastics, and refillable containers to reduce packaging waste and minimize environmental impact. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on minimalist packaging or zero packaging (e.g. solid products instead of liquid) and optimization to enhance recyclability and reduce resource consumption. Utilizing QR codes on packaging can offer an efficient solution for conveying sustainability messages without occupying excessive space on the packaging.
2024’s KEY TRENDS AND MARKET CONCEPTS:
Looking ahead to 2024, several overarching trends are expected to shape the natural cosmetics market. These include:
- Continued growth of the clean beauty movement, which has evolved beyond ‘free-from’ claims and natural ingredients to a wider set of ecological and ethical concerns, including ingredient transparency.
- ‘NeuroGlow’ refers to a global approach to beauty where mental well-being and physical appearance are interconnected, emphasizing a comprehensive connection between mind and skin.
- Inclusion has a powerful and very necessary place in an industry built on aesthetics. In the United States, 73% agree that the beauty industry plays on women’s insecurities and almost half of beauty consumers “say they have looked for/bought from brands with diversity or inclusive in the last year” (5). Consumers demand an industry aimed at all ages, races, genders, classes, and religions.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a significant role in the cosmetics industry, allowing for fast data-driven analysis of large datasets. This will enable companies to extract valuable insights, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. AI may also be used for personalized recommendations, virtual try-ons, skin analysis, formulation, and ingredient analysis.
REGULATORY FRAMEWORK AND EXPECTED CHANGES
The cosmetics industry can anticipate regulatory developments aimed at enhancing consumer protection, environmental sustainability, and product transparency. We are seeing how international bodies are working to improve the industry. Recently, we have seen how Chile (January 2024 (6)) and Canada (December 2023 (7)) have prohibited cosmetic testing on animals. Most recently, in March 2024, the European Union Directive aimed at empowering consumers for the green transition (8), a significant step in improving product labelling standards, providing more accurate and reliable advertising, and banning commercial malpractices entered into force with a 24-month transition period for Member States until application of the Directive from 27 September 2026.
Throughout 2024 work is expected to continue to finalise two legislative files: the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR (9)) and the Green Claims Directive (GCD (10)). The PPWR is a revision of the existing Directive but goes beyond its essential requirements (reduce waste, design requirements for materials and goods) to include also measures to reduce (over)packaging and packaging waste alongside actions to improve packaging design for reuse and recycling and to drive the uptake of recycled content. In March 2024 the Council presidency and the European Parliament’s representatives reached a provisional political agreement on a proposal for a regulation on packaging and packaging waste, which could mean publication of the Regulation by Q3 2024 with application of legislation 18-months after entry into force.
The GCD is a complimentary piece of legislation to the Directive on empowering consumers for the green transition. The GCD sets specific requirements for explicit environmental claims and labelling schemes, as well as promoting third-party certification via an ex-ante (pre-market) verification mechanism. In March 2024 the European Parliament voted strongly in favour of the joint ENVI/IMCO committee report; therefore, confirming its stance before negotiations on the final text that will take place after the EU elections in June. A provisional timeline for the GCD would be finalisation of the text in Q4 2024 or Q1 2025, with application 18-months after entry into force.
As the natural cosmetics industry continues to evolve, brands must adapt to changing consumer preferences, regulatory requirements, and market dynamics. By embracing sustainability, transparency, and innovation, cosmetics companies can not only meet the evolving needs of consumers but also contribute to a more sustainable and ethical beauty industry for the future.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
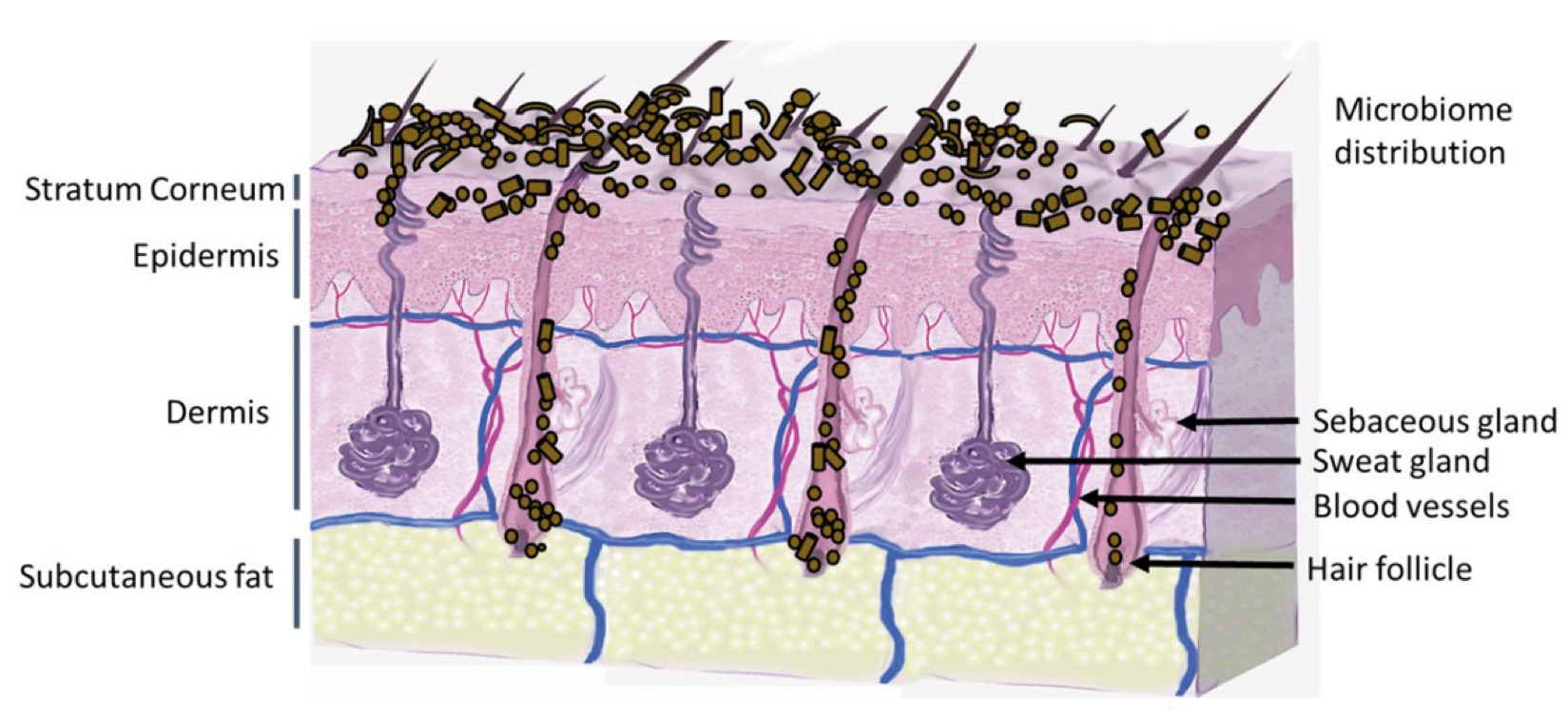
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- Euromonitor International, 2024. https://go.euromonitor.com/webinar-2024-consumer-trends-to-watch.html
- Euromonitor International, 2024. https://go.euromonitor.com/webinar-2024-consumer-trends-to-watch.html
- European Commission, 2020. https://circabc.europa.eu/ui/group/44278090-3fae-4515-bcc2-44fd57c1d0d1/library/b11ba10b-5049-4564-b47a-51a9bc9003c8/details?download=true
- UEBT https://uebt.org/resource-pages/deep-dive-on-beauty-and-biodiversity
- https://www.mintel.com/press-centre/63-of-americans-are-inspired-by-beauty-brands-that-show-diversity-in-advertising/
- https://www.bcn.cl/leychile/navegar?idNorma=1200504
- https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/f-27/
- https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=OJ:L_202400825
- https://environment.ec.europa.eu/publications/proposal-packaging-and-packaging-waste_en
- https://environment.ec.europa.eu/publications/proposal-directive-green-claims_en
