H3i 2024: Detergents - navigating ecological transition, opportunities, and challenges
GIULIO FEZZARDINI
Experienced Event Organiser and Chairperson
Content Writer – Consultant

??????????????????
“
“A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans”
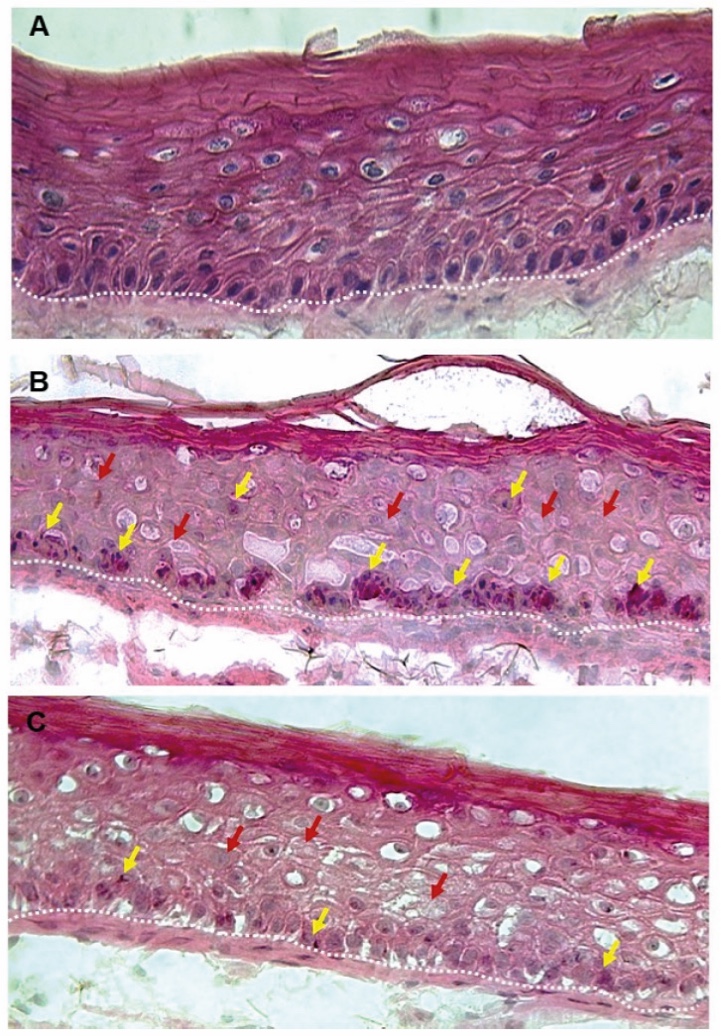
Figure 1. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
Materials and methods
Studies of major depressive disorder have been correlated with reduced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria and symptom severity has been correlated to changes in Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteriodes. Gut microbiota that contain more butyrate producers have been correlated with improved quality of life (1).
A study in healthy women providing probiotic yogurt for four weeks showed an improvement in emotional responses as measured by brain scans (2). A subsequent study by Mohammadi et al. (3) investigated the impacts of probiotic yogurt and probiotic capsules over 6 weeks and found a significant improvement in depression-anxiety-stress scores in subjects taking the specific strains of probiotics contained in the yogurt or capsules. Other studies with probiotics have indicated improvements in depression scores, anxiety, postpartum depression and mood rating in an elderly population (4-7).
Other studies have indicated a benefit of probiotic supplementation in alleviating symptoms of stress. In particular, researchers have looked at stress in students as they prepared for exams, while also evaluating other health indicators such as flu and cold symptoms (1). In healthy people, there is an indication that probiotic supplementation may help to maintain memory function under conditions of acute stress.
With approximately 800 visitors, 50% more than the previous year, H3i Italia, an event dedicated to chemistry in the domestic and industrial cleaning supply chain, achieved significant growth and acclaim in 2024.
As the scientific committee began brainstorming ideas on the new conference program, the theme of ecological transition within the cleaning supply chain emerged as a focal point, a sign of the common feeling of a sector that has always and increasingly been at the forefront of the challenges raised by the debate on sustainable development.
An increasingly complex debate. In the early years of its enunciation (from the 'Brundtland Report' of 1987, named after the coordinator of the World Commission on Environment and Development) 'sustainability' meant simplifying as much as possible, making new formulations more and more eco-friendly. Then the term was progressively declined in every aspect of our daily life until arriving at today's GREEN DEAL. This ecological transition encompasses a holistic approach to land and environmental policies, with renewable energies playing a pivotal role in fostering global sustainability.
The conference aimed therefore to explore the topic of sustainability in detergents through scientific presentations, case studies, and technical-commercial discussions. The event featured distinguished associations such as Federchimica (Assocasa-Aispec), AssICC, and AFIDAMP, the reference point for professional cleaning, which enhanced the conference with an insightful session.
To kick off the two-day event, interviews were conducted with various companies, posing questions such as:
What is your company's vision towards the green economy? what opportunities and challenges are you facing in achieving sustainability goals?
Key themes and insights from these interviews included:
WATER AND WATERLESS PRODUCTS: an increasingly precious resource due to the proven difficulties in water supply and water management resulting from climate change and increased demand, the subject of 'water' is now more sensitive than ever. Hence the effort to create concentrated and 'waterless' products. A wide range is available on the market today.
ECO FORMULATIONS, ECOLABEL, ECOCERT, ORGANIC PRODUCTS: the trend towards natural ingredients and eco-friendly formulations continues to gain momentum, accompanied by developments in probiotics for domestic and professional cleaning applications. However, there is a need for clarity on raw materials, such as the biobased definition for surfactants, and the real impact of environmental sustainability, which can be challenged by various factors such as logistics and transport.
Sustainable PACKAGING: companies are prioritizing sustainable packaging solutions, driving innovation, analysis of environmentally compatible materials, and development of increasingly virtuous recycling technologies.
ASSOCIATIONISM: increasingly crucial is the role of Associations in providing consultancy, assistance, advocacy, and cultural promotion contributing to COMPREHENSIVE COMMUNICATION strategies.
The EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT AND AWARENESS are vital for the manufacturer. Staff are first and foremost consumers and users of services. Employee involvement is crucial for fostering innovation and achieving shared sustainability goals within organizations. New professional figures such as the SUSTAINABILITY Manager are now consolidated in many companies.
ENERGY DIAGNOSES and investments in RENEWABLE ENERGY are pivotal for driving the development of transition towards sustainability: analyses, studies, company adaptations, new technologies underlying the company VISION.
DISRUPTION is the dominant dynamic of the historical period we are living through, from the outbreak of the pandemic to the crisis caused by the geopolitical turbulence that is still ongoing. Phenomena that have overturned paradigms in a short time, which usually is a result of a system evolution with a long gestation. However, the numbers recorded over the last five years highlight the cleaning sector's resilience and adaptability.
During interviews, FINANCING, NRP, and investment incentives emerged as critical considerations. Sustainability is indeed a beautiful concept, but it requires significant investments across various fronts, including technology and human resources.
A recurring concern highlighted by interviewees was the future regulatory landscape.
Many voices emphasized the need for SIMPLIFICATION, particularly in bureaucratic processes. However, there's widespread apprehension about impending legislative and regulatory changes that could become more restrictive, potentially influenced by the upcoming renewal of the European Parliament.
Election periods often witness ambitious promises, and the focus on 'GREEN' can evoke emotional responses. There's a risk of decisions driven by the pursuit of easy consensus, potentially influenced by parties not fully equipped to address sustainability issues.
Finally, in the lead-up to the conference, the Scientific Committee emphasized the importance of collaborative efforts, symbolized by the SHARED WORKTABLES.
Now more than ever collective collaboration is seen as essential, free from individualistic stances, fostering a unified approach that can promote shared visions to address significant challenges with determination and appropriate resources.
Perhaps the principle of SHARING is the key word that sums up the spirit of H3i 2024.
Surfactant Applications

The application area lends itself particularly well to the use of AI. Active today in this area is the US company Potion AI (6). The company provides AI-powered formulation tools for beauty and personal care R&D. Their offerings include Potion GPT, next generation ingredient and formula databases and AI document processing. Potion’s work could have a significant impact on the entire surfactant value chain, from raw material suppliers to end consumers. By using their GPT technology, they can help target work toward novel surfactant molecules that have optimal properties for specific applications. By using their ingredient and formula databases, they can access and analyze a vast amount of data on surfactant performance, safety, and sustainability. By using their AI document processing, they can extract and organize relevant information from patents, scientific papers, and regulatory documents. These capabilities could enable Potion AI's customers to design and optimize surfactant formulations that are more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient. A particularly interesting application for this type of capability is deformulation.
Deformulation is the process of reverse engineering a product's formulation by identifying and quantifying its ingredients. Deformulation can be used for various purposes, such as quality control, competitive analysis, patent infringement, or product improvement. However, deformulation can be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, as it requires sophisticated analytical techniques, expert knowledge, and access to large databases of ingredients and formulas.
AI can potentially enhance and simplify the deformulation process by using data-driven methods to infer the composition and structure of a product from its properties and performance. For example, AI can use machine learning to learn the relationships between ingredients and their effects on the product's characteristics, such as color, texture, fragrance, stability, or efficacy. AI can also use natural language processing to extract and analyze information from various sources, such as labels, patents, literature, or online reviews, to identify the possible ingredients and their concentrations in a product.
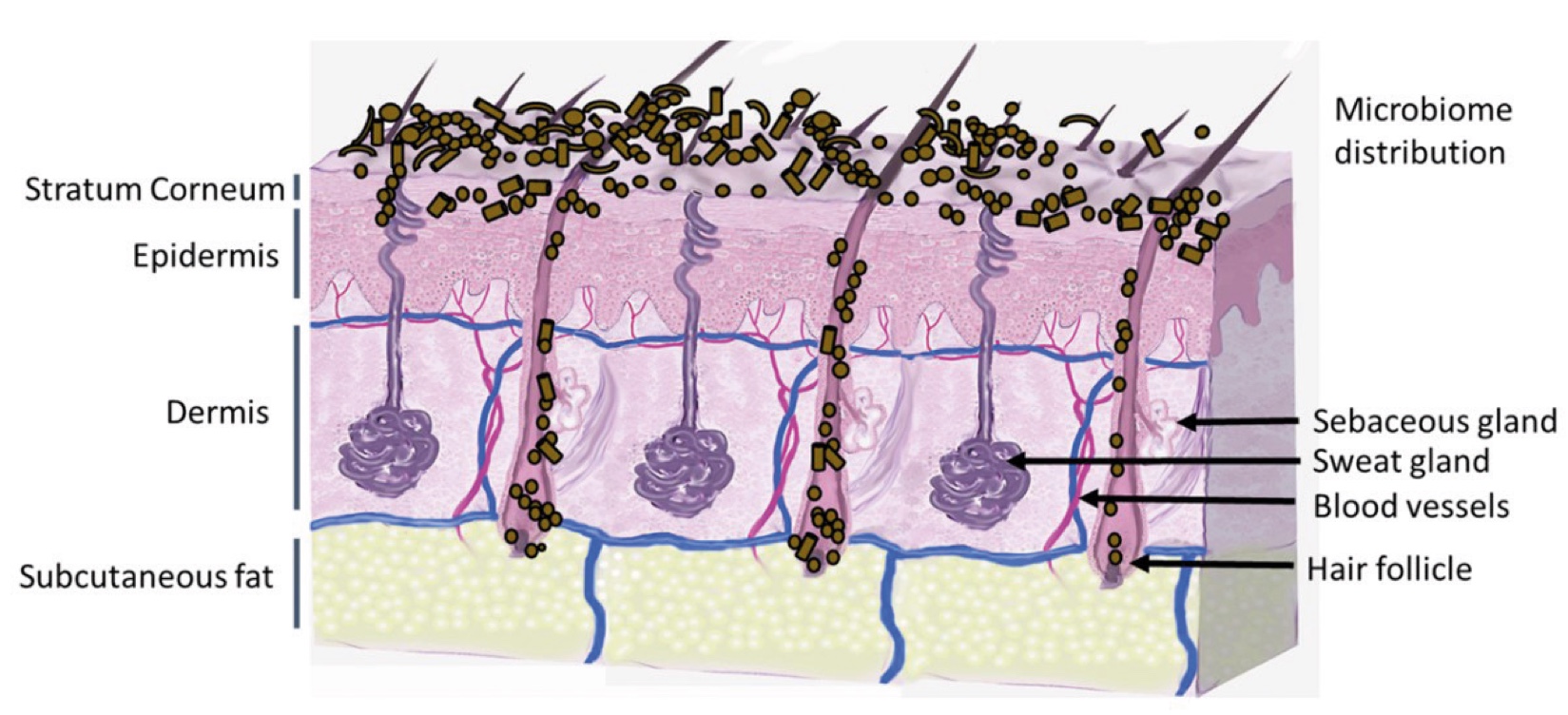
Figure 2. Skin Section with Microbiome. Most microorganisms live in the superficial layers of the stratum corneum and in the upper parts of the hair follicles. Some reside in the deeper areas of the hair follicles and are beyond the reach of ordinary disinfection procedures. There bacteria are a reservoir for recolonization after the surface bacteria are removed.
References and notes
- Inamadar, AC and Palit A. Sensitive skin: An overview. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 79:9-16, 2013.
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M. and Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 4;6:a016295, 2014.
- Qing, H. et al. Origin and Function of Stress-Induced IL-6 in Murine Models. Cell, 182,372-387, July 2023, 2020.
- Seite, Sophie. Hypothesis Letter. Skin sensitivity and skin microbiota: is there a link? Experimental Dermatology. 27:1061-1064, 2018.
- Hillion, M. et al. Comparative study of normal and sensitive skin aerobic bacterial populations. Microbiology Open. 2(6): 953-961, 2013.
- Zheng, Y. et al. Skin microbiome in sensitive skin: The decrease of Staphylococcus epidermidis seems to be related to female lactic acid sting test sensitive skin. Journal of Dermatological Science, v.97, n.3, p.225-228, 2019.
- Keum, H.L. et al. Structures of the skin microbiome and mycobiome depending on skin sensitivity. Microorganisms, 8, 1032, doi 10.3390, 2020.
- Frosch, P.; Kligman, A. and Duhring. A method for appraising the stinging capacity of topically applied substances. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 28(5):197-209, 1977
- Fillaire, F. et al Alternative in vitro models used in the main safety testes of cosmetics products and new challenges. Intl. Journal of Cosmetic. Sci,l
- Jarrin et al. Sensitive Skin: Insight Into Microbiota Composition and Comparison with Microbiota of Normal Skin. IFSCC Magazine. 23(1):45-54, 2020
- Kandi, V. et al. Emerging Bacterial infection: identification and clinical significance of Kocuria species. Cureus 8(8): e731, 2016.
- Sharma, C. et al. Polypharmacological properties and therapeutic potential of β-caryophyllene: a dietary phytocannabinoid of pharmaceutical promise. Curr. Pharm. Des.; 22 (21):3237-64. 2016
- Tóth, K. F. et al. Review: Cannabinoid signaling in the skin: therapeutic potential of the “C(ut)annabinoid” system. Molecules. 24; 918. 2019
- Su, T. et al. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors contribute to upregulation of β-endorphin in inflamed skin tissues by electroapuncture. Molecular Pain. 7:98, 2011.
- Ibrahim, M.M. et al. CB2 cannabinoid receptor activation produces antinociception by stimulating peripheral release of endogenous opioids. PNAS, vol. 102, 8, 3093-3098, 2005.
- [Pilozzi, A.; Carro, C. and Huang, X. Roles of β-endorphin in stress, behavior, neuroinflammation, and brain energy metabolism. Intl. J. Mol. Sci., 22,338, 2021.
- Gein, S.V. and Gorshkova, K. G. Evaluation of the effect of β-endorphin on IL-4 and ƴ-IFN Production by CD4+ lymphocytes. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 146.447-450, 2008.
- Loomis et al. A mixed community of skin microbiome representatives influences cutaneous process more than individual members. Microbiome, 9;22. 2021.
- Cogen, A.L.; Nizet, V. and Gallo, R.L. Skin microbiota: a source of disease or defence? Br.J.Dermatol., 158(3): 442-455, 2008.

