The rise of Collagen in Beauty: from animal sources to plant based innovation
Collagen is the buzzword in the ingestible beauty industry and also in the topical beauty sector. According to Global market Insights (1), the collagen market exceeded 4 USD billion dollars back in 2022 with an anticipated growth of 8% CAGR for the next 10 years. This makes collagen a steady trend with multiple applications and opportunities for innovation.
In this article I shall explore the collagen used by the cosmetic industry and a biomimetic plant collagen derived from biotechnology.
Collagen in the human body
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and a fascinating molecule. It is a combination of three helical polypetides chains, assembling into a twisted helix. Given its polymeric nature, there are twenty eight types of collagen in the human body (2), each one with different functions. The one present at highest concentration is collagen Type I which provides structure for bones, tendons and ligaments. Collagen type I is also produced within the skin and has a key structural role in the dermis, something consumers are very aware of, in their effort to keep the signs of aging at bay.
It is important to note that hydroxyproline is a characteristic amino acid to human collagen (3) as it helps to stabilise its triple helicoidal structure (4).
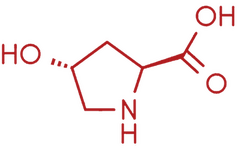
hydroxyproline
Collagen in the cosmetic industry
The cosmetic industry is spoiled with choice of collagen based actives, not only in terms of origin but also molecular size and structure. The most common source is animal, ie cow, pig and fish, but biotech and plant sources are also available. Because of the high molecular weight of pure collagen, it does not get absorbed through the skin however it provides humectant and moisturising benefits thanks to its film forming and water binding properties. Over time collagen can undergo maturation becoming less water soluble. For this reason a more popular form used in cosmetics is hydrolysed collagen, consisting generally of short polypetides and small peptides, which are readily water soluble. Depending on the molecular size and amino acid distribution the hydrolysed form can also penetrate into the skin and trigger collagen production. Hydrolysed collagen can also act as a humectant (5).
Campo biomimetic collagen
Using its proprietary biotechnology Campo developed the true human skin identical (THSI) Plant Collagen I (6). Derived from the Mimosa Tenuiflora, a tree commonly used in traditional medicine (7), the THSI comes with a consumer friendly INCI, ie Hydrolysed collagen, and a triple helix structure like the one found in human collagen, thanks to its high plant extracted hydroxyproline content.
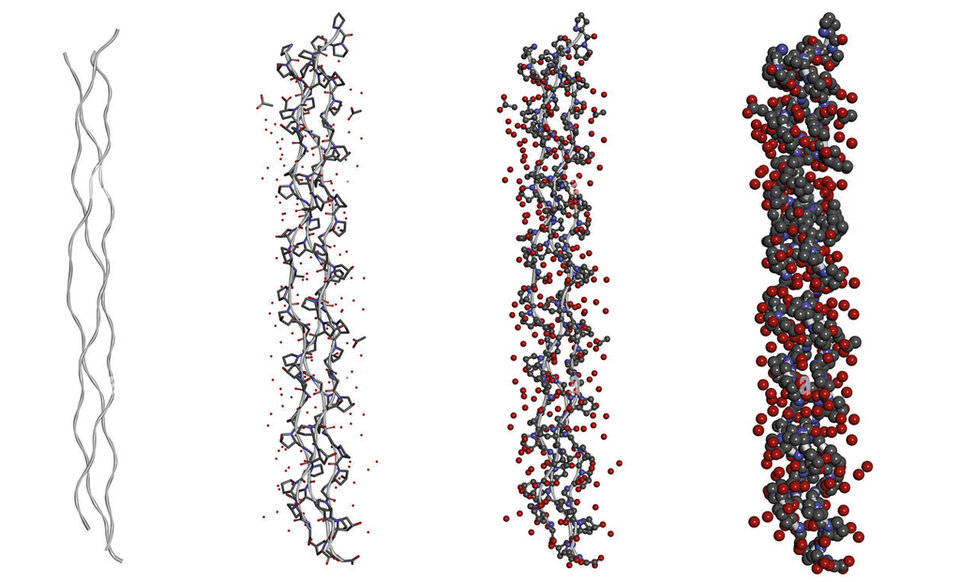
Hydration structure of triple helix collagen
The biomimetic helicoidal structure not only gives a really pleasant sensorial profile, with a velvety skin feel but also instant plumping effect thanks to the high moisture retention providing an hydrating film and boosting skin elasticity (see graph 1). When comparing the moisture retention properties of THSI Plant Collagen with other hydrolysed collagens that do not possess the same helicoidal structure one can appreciate the impact of a biomimetic helicoidal structure on skin hydration.
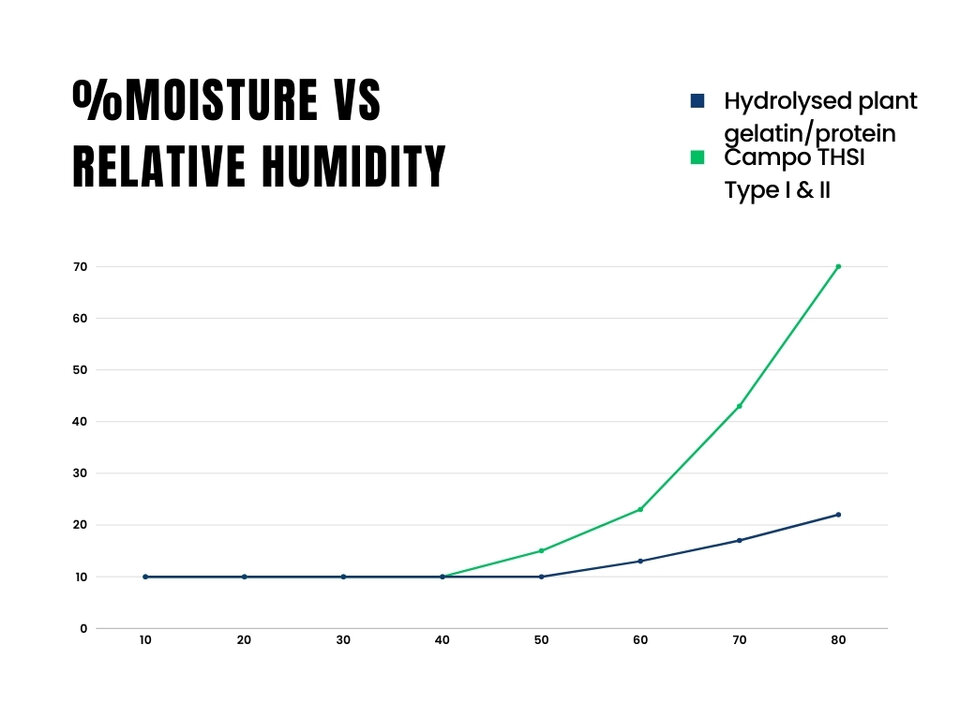
Graph 1.
Given the above characteristics the best applications for the Campo THSI Plant collagen are ones where velvety texture and instant moisturising are desirable such as skincare, suncare and haircare.
From a formulation perspective particular care is required to retain the unique helicoidal structure by avoiding ethanol, formaldehyde donors and hydrogen bond breakers. It is also helpful to formulate at pH above 5.
Campo THSI is Cosmos compliant and China approved, and it comes in two transparent and colourless liquid grades ie type I and type II.
Conclusions
As the collagen market continues to grow it is important to differentiate products going to market with unique ingredients delivering instant skin and hair benefits. The Campo THSI collagen is a very unique material with a biomimetic helicoidal structure and composition thanks to its high plant derived hydroxyproline content. The instant plumping effects thanks to its high moisture retention and the appealing INCI name, ie hydrolysed collagen, makes it ideal in a competitive market place in skin and haircare applications.
References and notes
- Global Market Insights, Collagen Market By Product (Gelatin, Peptides), By Source (Bovine, Porcine, Marine), By Dosage Form (Powder, Liquid, Capsule), By Application (Food, Healthcare, Nutraceuticals, Personal care & cosmetics) & Global Forecast 2023-2032, Report ID GMI 206. Mar 2023https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/collagen-market
- Fisher GJ, Varani J, Voorhees JJ. Looking older: Fibroblast Collapse and Therapeutic Implications. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144(5):666-672.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2887041/#:~:text=Fibroblasts%20are%20developmentally%20programmed%20to,matrix%20including%20type%20I%20collagen.
- Tarnutzer, K., Siva Sankar, D., Dengjel, J. et al. Collagen constitutes about 12% in females and 17% in males of the total protein in mice. Sci Rep13, 4490 (2023)
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-31566-z#:~:text=Hydroxyproline%20is%20relatively%20unique%20to,reviewed%20in22%2C23) - Shoulders MD, Raines RT. Collagen Structure and Stability. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:929-958.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2846778/ - Sionkowska A, Adamiak K, Musiał K, Gadomska M. Collagen Based Materials in Cosmetic Applications: A Review. Materials (Basel). 2020 Oct;13(19):4217.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7578929/ - https://www.campo-research.com/
- Majeed I, Rizwan K, Ashar A, Rasheed T, Amarowicz R, Kausar H, et al. A Comprehensive Review of the Ethnotraditional Uses and Biological and Pharmacological Potential of the Genus Mimosa. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7463.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8307580/\